Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
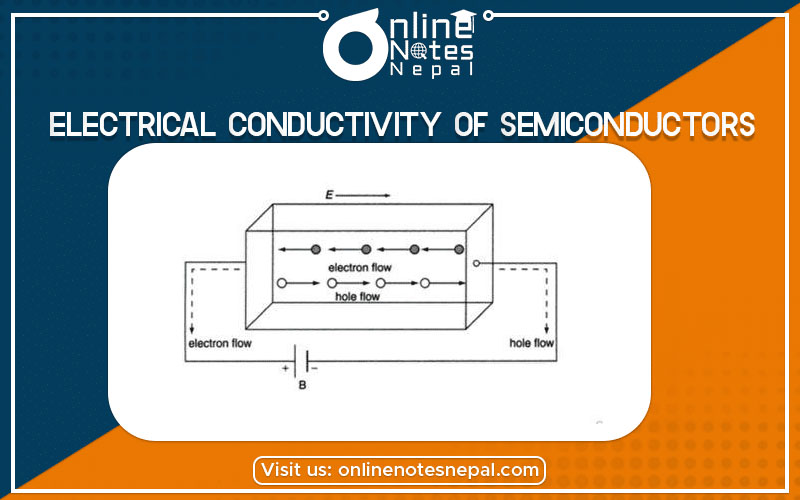
Electrical Conductivity of Semiconductors is determined by the number of free electrons and holes per unit volume and on the rate at which it carries. In an intrinsic semiconductor, there exists an equal number of free electrons and holes. When an electric field is applied to the semiconductor, valence holes drift in the direction of the applied field. Whereas, conduction electron drifts in the opposite direction of the applied field. The drifting of both electrons in the conduction band and holes in the valence band contribute to current in one direction.
Therefore, the total no. of current density in the semiconductors is,
J = n e vde + p e vdh
Where, n = no. of electron concentration in the conduction band
P = holes concentration in the valence band
vde = drift velocity of electrons
vdh = drift velocity of holes
Since,
µ = vd/E
vd = µE
Therefore, J = n e µe E + p e µh E
σ E = (n e µe + p e µh) E
σ = n e µe + p e µh
where µe and µh are electron and hole mobilities.
In an intrinsic semiconductor, the density of holes in the valence band is equal to the density of electrons in the conduction band.
i.e. n = p = ni
Hence, σ = e ni (µe + µh)
Now,
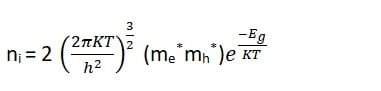
where Eg is the energy gap = Ec = Ev
Therefore,
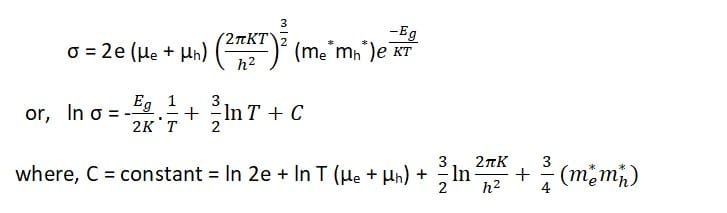
where, C = constant = ln 2e + ln T (µe + µh) +
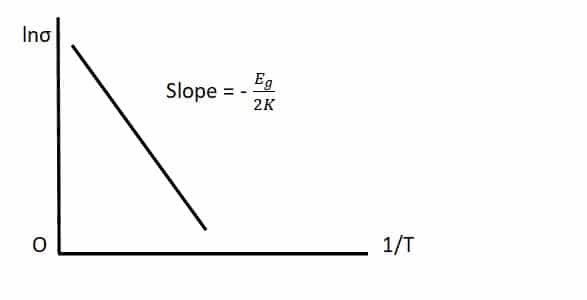
We also assume that electron and hole mobilities are independent of the temperature. The main variation in ln σ is due to the term containing 1/T.
If the graph is plotted, it will look like,
The conductivity in the n-type semiconductor occurs due to the electrons in the conduction band. This is given by,
σ = n e µe
Now,
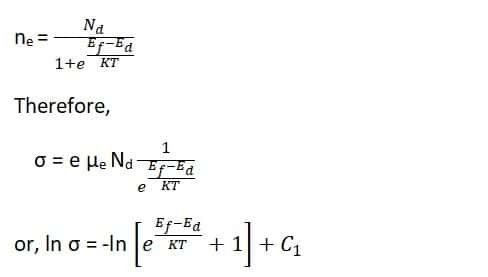
Here, C1 is constant in C1 = ln e µe Nd,
Nd is the no. of donor atoms per unit volume.
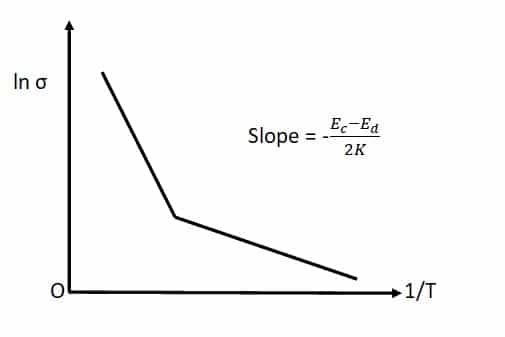
If the graph plotted, it will look like,
The conductivity of a p-type semiconductor is due to the holes in the valence band. It is given by σ = np µh
Now,
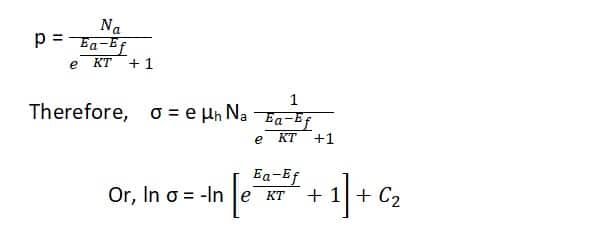
Equaton
Where, C2 is a constant = ln e µh Na, Na is the number of acceptor atoms per unit volume at the acceptor level.
If we plot a graph, it behaves similarly to that of the n-type semiconductor.