Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
1. Specific conductance-
The specific conductance of a solution is the conductance due to one cm3 of the solution. As the solution is diluted the number of ions per cm3 of the solution decreases so specific conductance decreases with an increase in dilution. The degree of ionization increases and the number of ions also increases but this increase will be less than the decrease in the number of ions so the net result is the decrease in specific conductance with an increase in dilution.
2. Equivalent conductance-
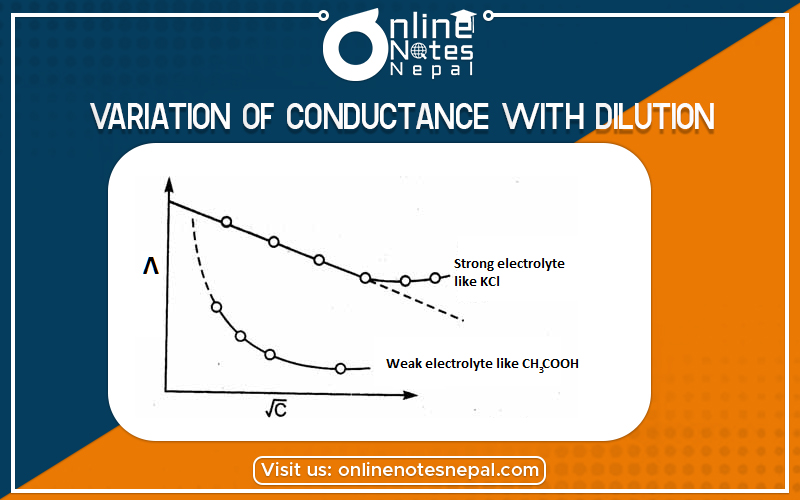
Equivalent conductance or equivalent conductivity is the number of ions produced by one gram equivalent of the solute. The variation of equivalent conductivity can be explained in two cases.
In the case of weak electrolyte the total number of ions produced by one gram equivalent of solute increase after dilution. As there is no limitation for the volume of the solution so equivalent conductance increases with an increase in dilution.
In the case of strong electrolytes, they are almost completely ionized so there are hard increases in the number of ions after dilution. It indicates that there is no alteration in the conductivity value slightly increases after dilution. As the solution is diluted ions become far apart. And thus the electrostatic force of attraction decreases there in the case movement of ions. As the moment of ions increases so conductivity value also increases.
Therefore the Variation of Conductance with Dilution is explained above.