Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
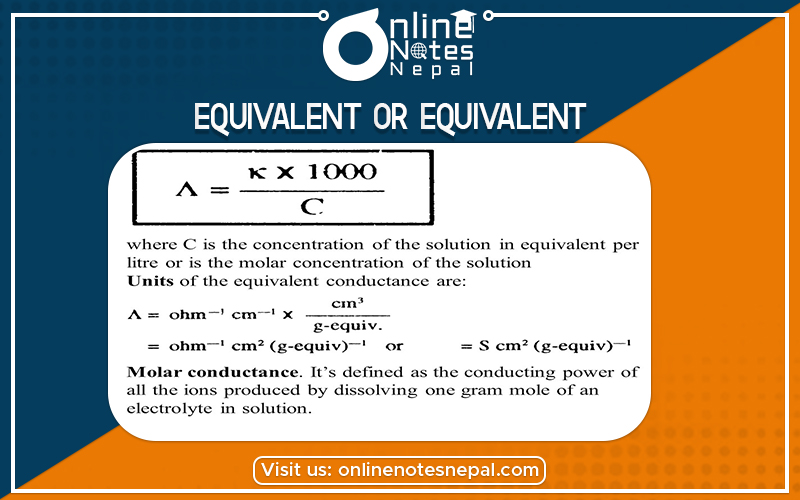
Equivalent conductance or Equivalent conductivity is defined as conductance of a certain volume of solution containing one gram equivalent of the substance when the whole solution is placed between two parallel electrodes separated by 1cm apart and contained large enough between the whole solution.
Let ‘V ml’ be the volume of solution containing 1gm equivalent to the solute and ‘k’ be the specific conductance of a solution then, equivalent conductance (λ) can be given as:
λ = K × V
If CN is the concentration of the solution in normality then the volume of solution containing 1gm equivalent of solute is 1000/CN.
Therefore, λ= K × 1000/CN
In the CGS system, it is measured in siemen cm2eq-1
Molecular conductance or molecular conductivity:
Molecular conductance or molecular conductivity is defined as conductance of a certain volume of solution containing one gram molecular weight of the substance when the whole solution is placed between two parallel electrodes. Separated by 1cm apart and contained large enough between the whole solution.
Let “V ml” be the volume solution containing 1gm molecular weight of solute and k be specific conductance of solution then molecular conductance (w) can be given as;-
W= k × V
If CM is the concentration of the solution in molarity the volume of solution contains 1gm mole of solute is 1000/CN
or, k × 1000/CN
In the CGS system it is measured in siemen cm2mole-1
The conductance or resistor of a solution depends on the distance between the electrodes and the area of the electrodes.
We have,
R= resistance in ohm
ϱ= specific resistance
L= distance between the electrodes
A= area of the electrodes
For a given cell the distance between the electrodes and the area of the electrodes is found to be constant. Hence, the ratio is called cell constant.
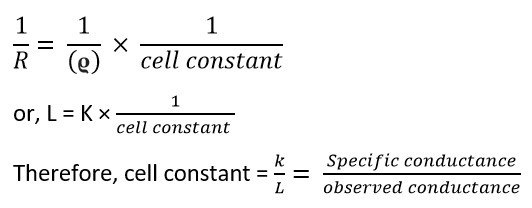
Therefore, R= ϱ × l/A
or, R = ϱ × cell constant………. (iii)
where cell constant = l / A = cm / cm² = cm⁻¹
In the CGS system, it is measured per cm. Taking the reciprocal of equation (ii)