Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
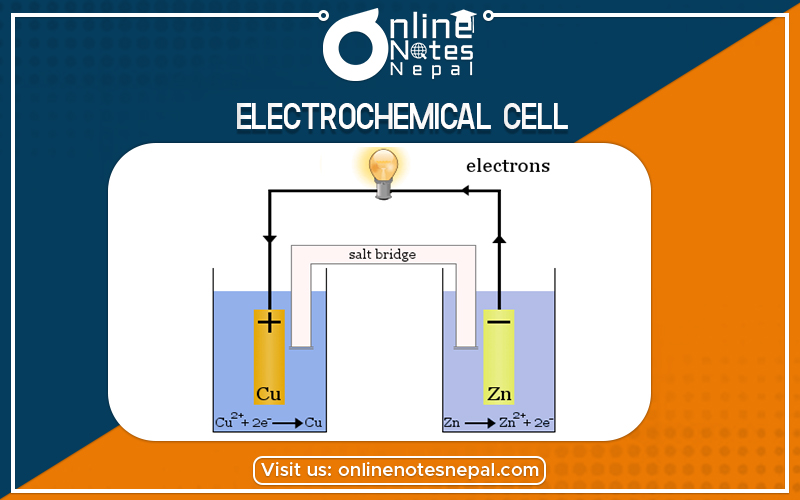
An electrochemical cell is a system consisting of two different electrodes dipped in the same or different electrolytic solution in electrical communication. It is of two types:-
The electrochemical cell in which chemical reaction occurs bypassing of electricity is called electrolytic cell.
The electrochemical cell in which electricity generates by means of the chemical reaction is called a galvanic cell or voltaic cell.
Construction of Galvanic cell
pic
let us consider two beakers in which one beaker contains a zinc rod dipped in zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) solution and another beaker contains a copper rod dipped in CuSO4 solution. Both these beakers are connected with the help of the salt bridge and two electrodes are connected to a voltmeter or ammeter. The cell so formed is called the Galvanic cell or Voltaic cell.
The metallic conductor in contact with its solution is called electrode and the compartment containing the electrode and the electrolytic solution is called a half cell. The cathode is always written on the right-hand side while the anode is always written on the left-hand side. The cell notation can be given as
Zn(s)/Zn++(aq) // eu++(aq)/Cu(s)
When the connection is complete a potential difference develop which is called ENF or electromotive force. The zinc electrode is the anode and the copper electrode is the cathode. Oxidation and reduction taking place at these electrodes are
Zn(s) Zn++(aq) + 2e–(oxidation half-reaction) at anode
Cu++ (aq) + 2e Cu(s) (Reduction half-reaction) at cathode
Zn(s) + Cu++(aq) Zn++(aq) + Cu(s) this is called net reaction.
In a galvanic cell, electrons flow through the external circuit from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode). Since the oxidation potential to the electrode of lower oxidation potential. The inner circuit is competed by the flow of ions from one solution to another solution through the salt bridge. A single line(/) indicates the interface between the two different faces such as (//) indicates the physical separation such as a salt bridge or porous diaphragm in which electrical conduction takes place.
If we change any of the electrodes then the emf of the electrode will also change because the electrode potential of the individual electrode will also be changed.