Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinematics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a process occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction mechanism and transition states as well as the construction of mathematical modes that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction.
The brain of chemistry deals with the study of the rate of a chemical reaction and the mechanism by which the reaction proceeds are called chemical kinematics.
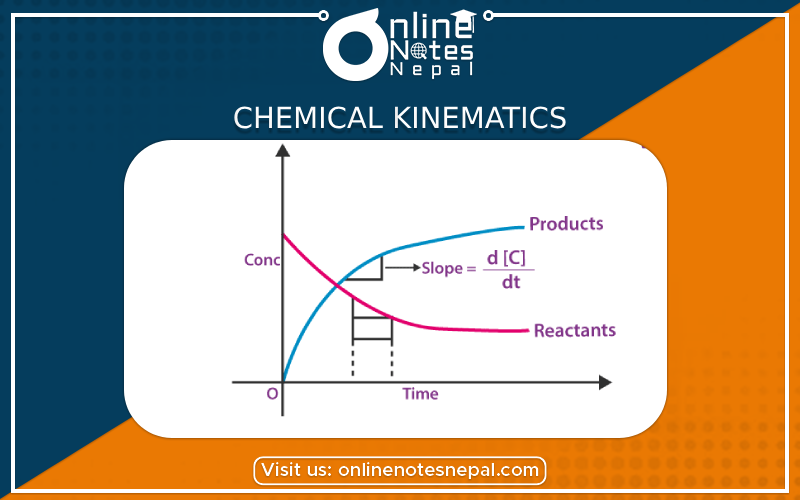
Concept of Rate of Chemical Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction is defined as the change in concentration of reactant or product with
pic
It is measured in molelitr–S–
Lets us consider the following types of chemical reactions
.pic
Here ‘-sign’ indicates that a decrease in concentration at A with respect in time, while ‘+’ sign indicates the increase in the concentration of ‘B’ with respect to time.
Types of Rates of Chemical Reactions
There are three types of rate of chemical reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction due to the change in concentration of reactant or product over a specific interval of time is called the average rate of a chemical reaction. It is denoted by av.
Lets us consider the following type of chemical reaction
C→D
pic
pic