Published by: Nuru
Published date: 27 Jun 2021
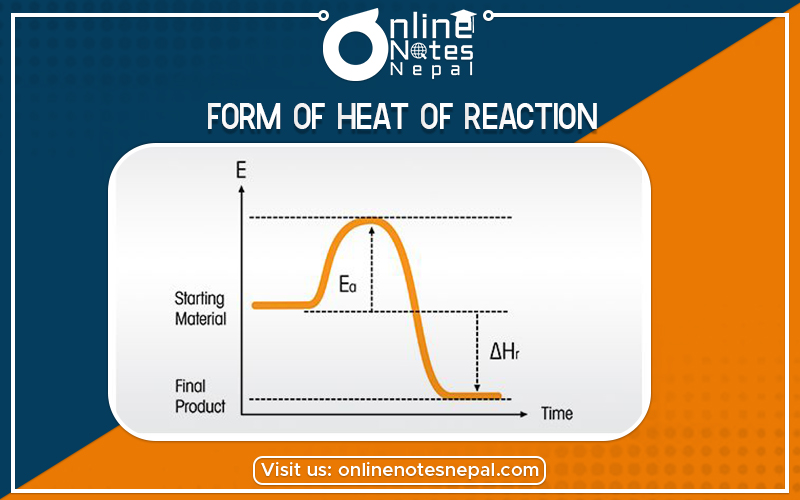
Form of heat of reaction are caused by neutralization, combustion, vaporization, and formation.
Different Forms of the Heat of Reaction
The different form of heat of reaction are:
1)Heat of Neutralization
2)Heat of combustion
3)Heat of vaporization
4) Heat of formation
1) Heat of Neutralization
The heat of neutralization is defined as the change in enthalpy when one acid is neutralized by a base and vice versa. For example ‘The Heat of Neutralization of HCL is -13.7 kcal.
HCL + NaOH→ NaCl + H2O, ), ΔH=-13.7 kcal
2) Heat of combustion
The heat of combustion is defined as the change in enthalpy when one mole of a substance is completely oxidized. For example ‘The Heat of combustion of methane is -212.7 kcal which can be shown by the following reaction.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2+ 2H2O, ΔH=-212.7 kcal
3) Heat of Vaporization
The heat of vaporization can be defined as the change in enthalpy when one ole of substance changes from its liquid state of vapor form. For example ‘Heat of vaporization of water is 10.5 kcal which can be shown by the following reaction
H2O (l) →H2O (g), ΔH=-10.5 kcal
4) Heat of Formation
The heat of formation is defined as the change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements. For example ‘Heat of formation of hydrogen gas combines with chlorine gas to give hydrogen chlorine gas evolving 44 kcal of heat.
H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g), ΔH=-44 kcal
Here -44 kcal of heat is not the heat of formation of HCl because this amount of heat is evolved when 2 moles of HCL is produced. Sp=o Heat of formation of HCL is -22 kcal.
These are the different forms of heat of reaction.