Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
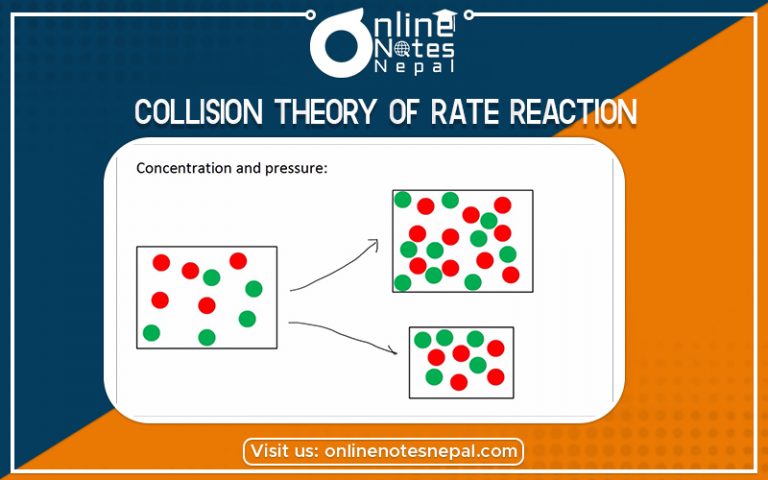
Collision theory of rate reaction states that when suitable particles of reactant hit each other, only certain fraction of the collisions cause chemical change.; these successful changes are called successful collisions. The successful collisions must have enough energy, also known as activation energy, at the moment of impact to break the pre-existing bonds and form all new bonds. This results in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactant particles or raising the temperature which brings about more collisions and hence more successful collisions, therefore, increases the rate of a reaction. Collision theory was proposed independently by Max Trautz in 1916 and William Lewis in 1918.