Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
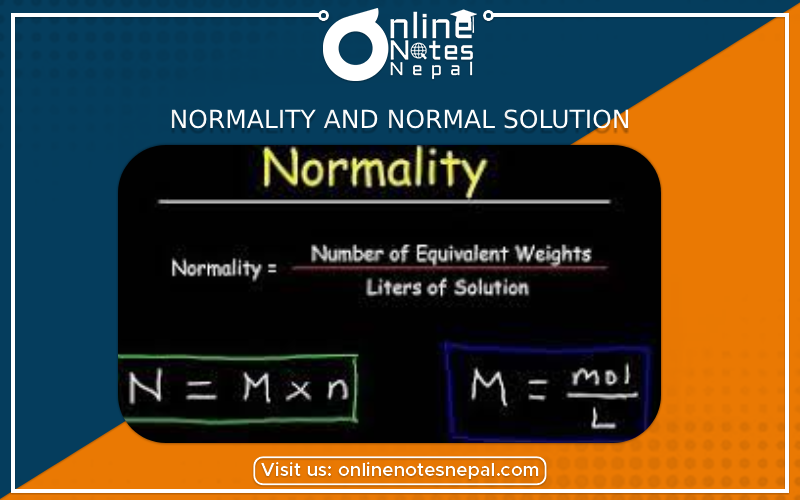
Normality of a solution is defined as the number of gram equivalent of solute dissolved in 1 litre of solution. The normality of a solution is the gram equivalent weight of a solute per litre of solution. It may also be called the equivalent concentration. … For example, the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution might be expressed as 0.1 N HCl. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:-
Normality= (No. of gram equivalent of solute) / (Volume in liters of a solution)....(i)
If one gram equivalent of solute dissolves in one litre of a solution then such type of solution is called one normal solution or simply a normal solution.
we know that,
pic
Molarity and Moral solution:-
The morality of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre of a solution. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:-
Molarity = (no. of moles of solute) / Vol. in liters of a solution....(iv)
If one mole of solute dissolves in one litre of the solution then such type of solution is called one molar solution or simply molar solution.
We know that,
pic
From eqn (iii) and (vi) we get,
Normality × equivalent weight= molarity × molecular weight….. (vii)
This is the required expression for the relation between normality and molarity.
From eqn (vii)
Normality × Eq. wt = molarity × mol. Wt
or, Normality = Molarity × (Mol.Wt/ Eq.Wt)
or, Normality = Molarity × Acidity (In case of base)
or, Normality = Molarity × Basicity (In case of acid)
\