Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
Entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the system’s disorder, that is a property of the system’s state, and that varies directly with any reversible change in heat in the system and inversely with the temperature of the system. The entropy of a gaseous substance is higher than that of liquid and solid. Thus the order of Entropy’s of various forms of substance can be given as,
S gas >> liquid > solid
It is a state function because of its magnitude depends upon the initial and final state of the system but doesn’t depend upon the path by which it has been reached. Entropy’s change in a substance can be given as,
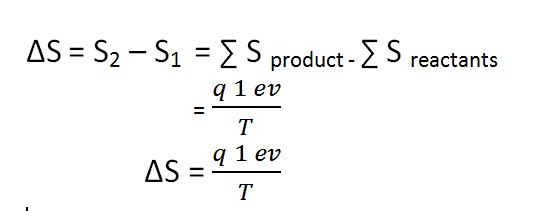
In the SI system, it is measured in J/K.
It changes during the following phase of transformations:-
It is defined as the difference between the Entropy of one mole of a substance from its liquid state to solid-state at the melting point.
∆S fusion = S liquid - S solid
During Phase transformation, heat equals to the enthalpy of fusion is absorbed (i.e.∆H fusion)
q rev = qrev = ∆Hfusion
Now,
∆S fusion = ∆Hfusion / T fusion
It is defined as the difference between one mole of a substance from its liquid state to a gaseous (vapor) state at the boiling point.
∆Svaporization = S vapor – Sliquid
During the phase, transformation heat equals to vaporization is absorbed.
q rev = ∆H vaporization
Now, ∆S vaporization = ∆H vaporization / T vaporization
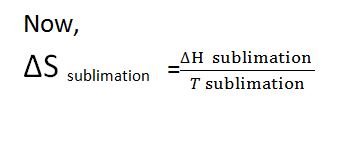
It is defined as the difference between the one mole of a substance from its solid state to the vapor state at the transformation state. During phase transformation, heat equals the enthalpy of sublimation is absorbed ( ∆Hsublimation).