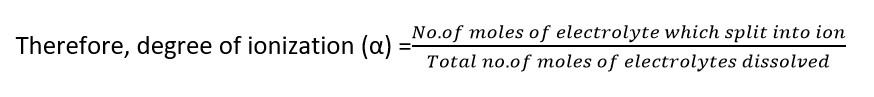Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
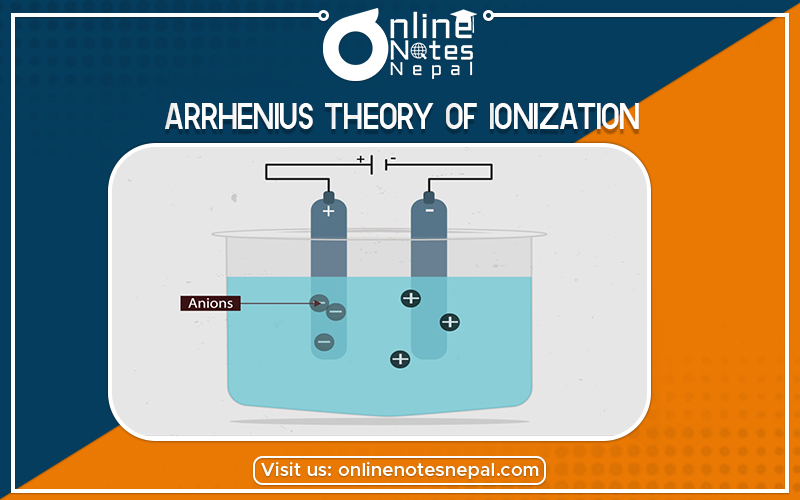
Arrhenius Theory of Ionization Concept:
Arrhenius theory introduced in 1887 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. It states that acids are substances that dissociate in water to yield electrically charged atoms or molecules, called ions, one of which is a hydrogen ion (H+), and that bases ionize in water to yield hydroxide ions (OH−). Some examples include: When sodium and chlorine combine to make salt, the sodium atom gives up an electron resulting in a positive charge while chlorine gets the electron and becomes negatively charged as a result.
Some fundamental postulates of Arrhenius theory of ionization-
Degree of Ionization ( α) = no. of moles of electrolytes which split into ion / total no. of moles of electrolytes dissolved
The electrical conductivity of the electrolyte in the solution is the number of ions produced by them.