Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
The rate law or rate equation for a chemical reaction is an equation that relates the reaction rate with the concentrations or partial pressures of the reactants. For the general reaction aA+bB→CaA+bB→C with no intermediate steps in its reaction mechanism, meaning that it is an elementary reaction.
Let us consider the following type of chemical reactions.
aA + bB + cC → products
The rate law of this reaction can be givens
r = k [A]x [B]y [C]z
Where,
r = rate of chemical reaction
k = rate constant
x = order of reaction with respect to A
y = order of reaction with respect to B
z = order of reaction with respect to C
Hence, Rate law or rate equation is defined as the chemical equation which shows how the rate of a chemical reaction is related to the concentration of each of the reactants with power as ordered. The value of x,y, and z are obtained from the experiment so it is an experiment so it is an experimental parameter. The values x, y, and z may or may not be equal o the coefficient of reactants.
Rate constant
Let us consider the following type of chemical reactions.
A+ B → products
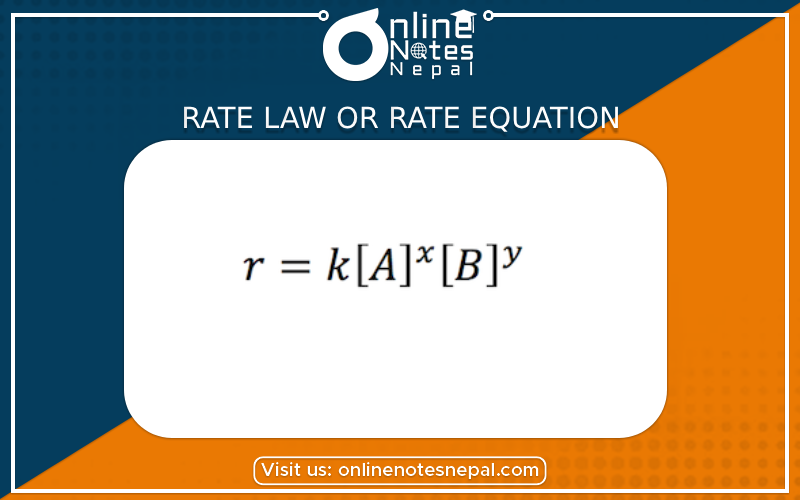
The rate law of this chemical reaction can be written as,
r = k [A]x [B]y
Where,
r = rate of chemical reaction
k = rate constant
x = order of reaction with respect of A
y = order of reaction with respect to B
If [A] = [B] = molelit-1 i.e.
Hence, the rate constant is defined as the rate of chemical reaction in which the concentration of each of reactant is found in be molelit-1 i.e. unity
If x=y=0,
Then,
r = k
Hence, the rate of constant can also be defined as the rate of chemical reaction having zero order of a reaction.