Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
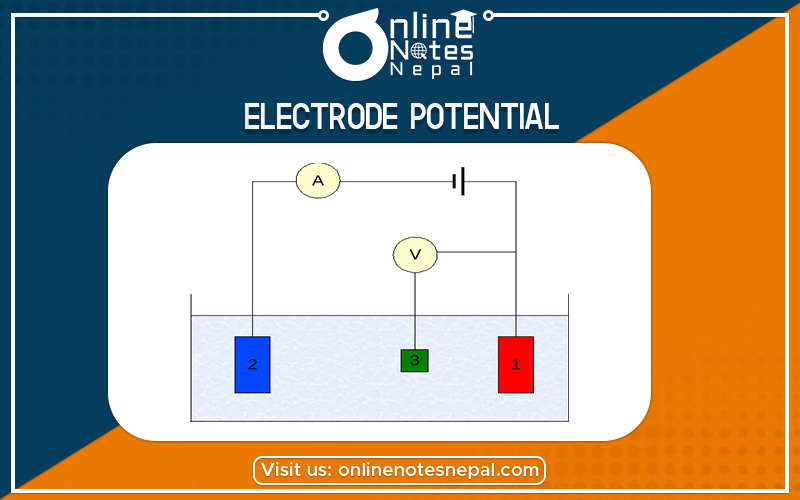
The differences set up between the metal electrode and its electrolytic solution is called electrode potential.
Single electrode potential is originated by the separation of charges between the metal electrode and its electrolytic solution.
When a metal is dipped into a solution of its own at a certain concentration its atoms either lose an electron to the solution and the metal itself becomes a positively charged electrode with respect to the solution or some of positively charged ion gain electrons and gets converted into the neutral atoms. This process causes the separations of charges.
Similarly, if the metal ions have a relatively greater tendency to take electrons from the electrode the process is reversed which causes the separation of charges.
The magnitude depends on the following three factors:-
It is defined as the potential difference developed at the metal solution interface when the concentration of the solution is 1 mole per liter at 25 degrees Celsius is called. Different metals and non-metals have different values of standard.
The hydrogen gas is manipulated at 1 atm and the concentration of H1 ion in solution is one mole is called standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). The emf of the standard hydrogen electrode is found to be 0.00V so it is used as a reference electrode for measuring the emf of the unknown electrode.
The series in which standard electrode potential of different electrodes are arranged in the increasing of their values is called electrochemical or emf or activity series.