Published by: Nuru
Published date: 27 Jun 2021
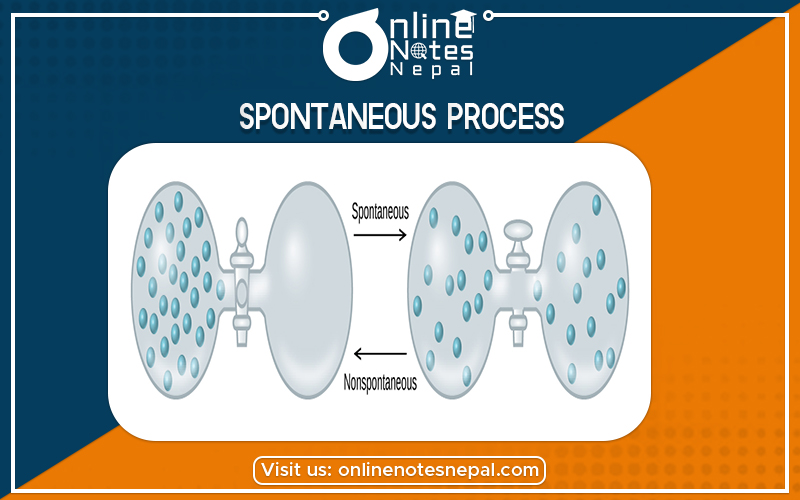
The step which has a natural tendency to take place on its own without the help of any other external agency is called a spontaneous process. It is one that occurs on its own, without any energy input from the outside. For example, a ball will roll down an incline; water will flow downhill; ice will melt into the water; radioisotopes will decay, and iron will rust. No intervention is required because these processes are thermodynamically favorable. In other words, the initial energy is higher than the final energy.
Note that how quickly a step occurs has no bearing on whether or not it is spontaneous: It may take a long time for rust to become obvious, yet it will develop when the iron is exposed to air. A radioactive isotope may decay instantly or after millions or even billions of years; yet, it will decay.
Whereas The reverse is a nonspontaneous process: Energy must be added in order for one to occur. For example, rust doesn’t convert back into iron on its own; a daughter isotope won’t return to its parent state.
Some other examples of it are given below;