Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
Gibbs free energy which is also known as Gibbs function or Gibbs energy or free enthalpy is a quantity used to measure the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are constant. Gibbs free energy is denoted as G.
This property was determined by Josiah Willard Gibbs in 1876 when he was conducting experiments to predict the behaviour of systems when combined together or whether a process could occur simultaneously and spontaneously. Gibbs free energy was also previously known as “available energy.”
Gibbs free energy is equal to the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature and entropy. The equation is given as;
G = H – TS
Where,
G = Gibbs free energy
H = enthalpy
T = temperature
S = entropy
Gibbs free energy is a state function hence it doesn’t depend on the path. So change in Gibbs free energy is equal to the change in enthalpy minus the product of temperature and entropy change of the system.
ΔG=ΔH-Δ(TS)
If the reaction is carried out under constant temperature{ΔT=O}
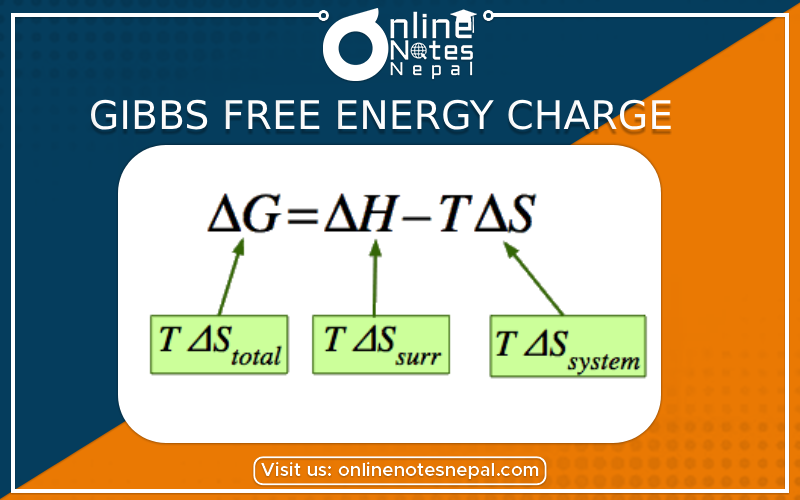
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS
This equation is called the Gibbs Helmholtz equation
ΔG>0; the reaction is non-spontaneous and endergonic
ΔG<0; the reaction is spontaneous and exergonic
ΔG=0; reaction is at equilibrium
Note: