Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
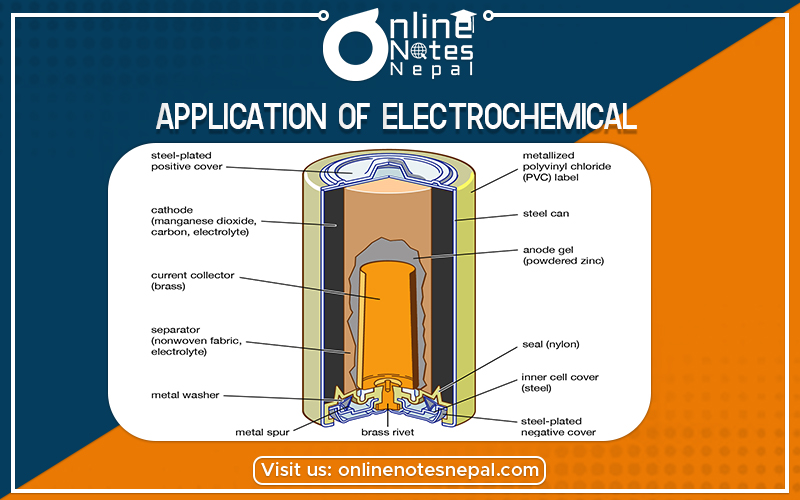
Application of Electrochemical are as follows:
2. To compare the relative activity of metals- Smaller the standard reduction potential of metal, the more easily it can lose the electron, and hence, the greater is its reactivity thus a metal with lower reduction potential can displace metal with higher reduction potential from the salt solution.
3. To calculate EMF of given galvanic cell- Galvanic cell is based on a reaction which can be observed into two half-reaction
The emf of the galvanic cell can be given as:-
EMF of cell= standard electrode potential of cathode- standard electrode potential of the anode
i.e. E degree of cell= Eocathode – Eoanode
4. To predict whether a metal will produce Hydrogen gas from dilute acid or not- A metal that has a strong tendency to lose an electron to form metal ions will displace H+ ions from the acid solution and thus will produce hydrogen gas.
M(s) + 2H+(from dil.acid)→H++(aq) + H2↑
Greater the value of standard reduction potential of metal smaller its tendency to lose the electrons to form metal ions and hence smaller its tendency to displace H+ ions or form water to produce hydrogen gas.
5. To see whether a given redox reaction is feasible or not EMF of the cell based on the given redox reaction is calculated. If EMF is found to be positive then the Galvanic cell does work and if EMF is found to be negative then given Galvanic does not work.
Therefore the Application of Electrochemical or Emf or Activity Series has explained above.