Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
Thermodynamics is the branch of physical science that deals with the relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, of the relationships between all forms of energy. Some Thermodynamics and Their Definitions are given below.
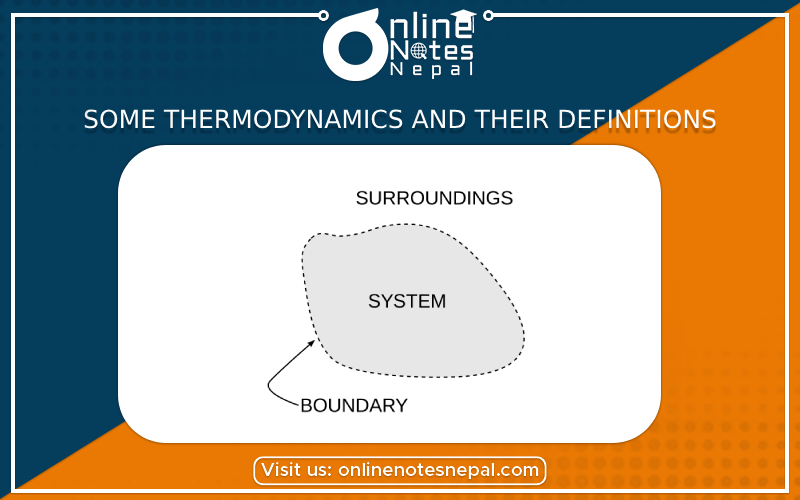
System
The part of the universe which is under study is called the system. A system may be very simple like water is taken in a beaker or may be very complex like the digestion of food.
Surrounding Environment
The rest part of the universe or environment around the system is called the surrounding. Surrounding means all other things that can interact with the system.
Boundary
Anything which separates the system from the surrounding is called boundary.
Depending upon a system that interacts with the surrounding system may be classified into 3 types.
1)Close system
2) Open system
3) Isolated system
State of a System
The parameters or properties which determine the state of the systems are pressure, temperature, volume, mass, and composition. These parameters are called state variables because any change in these parameters will also change the state of a system.
State function
A physical quantity is said to be a state function if its magnitude depends on the state of a system (initial and final) but not upon the path by which it has been reached.
state variables are of two types
1) Extensive properties
2) Intensive properties
1) Extensive Properties
Properties of a system whose magnitude depends upon the mass or quality of the substance are called extensive properties. For example mass, length, volume, etc.
2)Intensive Properties
Properties of a system whose magnitude doesn’t depend upon the mass or quantity of the substance are called intensive properties. For example temperature, refractive index, etc.
Therefore these are some definitions of thermodynamics.