Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021

In chemistry, it is a core concept in physical chemistry. Key Takeaways: Entropy Entropy is a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system. The value of entropy depends on the mass of a system. It is denoted by the letter S and has units of joules per kelvin. Entropy can have a positive or negative value. According to the second law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a system can only decrease if the entropy of another system increases.
A spontaneous process is the time-evolution of a system in which it releases free energy and it moves to a lower, more thermodynamically stable energy state. The sign convention for free energy change follows the general convention for thermodynamics measurements, in which a release of free energy from the system corresponds to a negative change in the free energy of the system and a positive change in the free energy of the surroundings.
let us consider a system that is at a higher temperature ‘r’ than a total of its surrounding temperature ‘T2’. Let us consider q amount of heat is irreversibly supplied from the system to the surrounding. The change in entropy can be calculated as.
The decrease in entropy of a system
i.e. -q / T1
And, the increase in entropy of the surrounding
i.e. +q / T2
The total entropy change i.e. ∆S total can be given as:
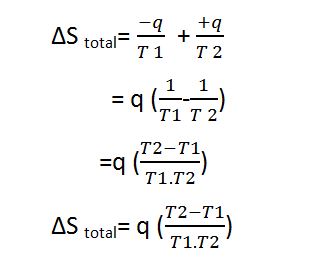
Since T1 is greater than T2 so T1-T2 is always found to be positive and the process is a spontaneous process.
If ∆S total> 0, the process is spontaneous in a direction as described with the condition. If ∆S total= 0, the process is equilibrium in nature, and if ∆S total<0, the process is non-spontaneous in a direction as described with the condition.
Therefore this is Entropy Criterion and Spontaneity.