Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
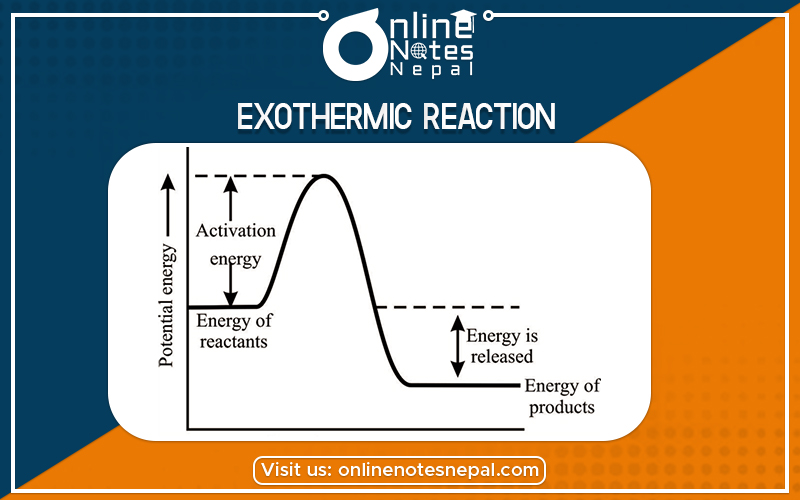
The chemical reaction in which heat is released or evolved is called exothermic. In such a reaction, ΔH is negative which indicates the enthalpy of products is less than the Enthalpy of the reactant.
The chemical reaction in which heat is released or evolved is called exothermic. In such a reaction, ΔH is negative which indicates the enthalpy of products.
It is a chemical reaction that releases energy through light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction.
Expressed in a chemical equation,
reactants → products + energy.
Exothermic type of reaction also means “Exo” (derived from the Greek word: “έξω”, literally translated to “out”) meaning releases and “thermic” means heat. So the reaction in which there is the release of heat with or without light is called an exothermic reaction.
The energy profile diagram for it can be given as:-
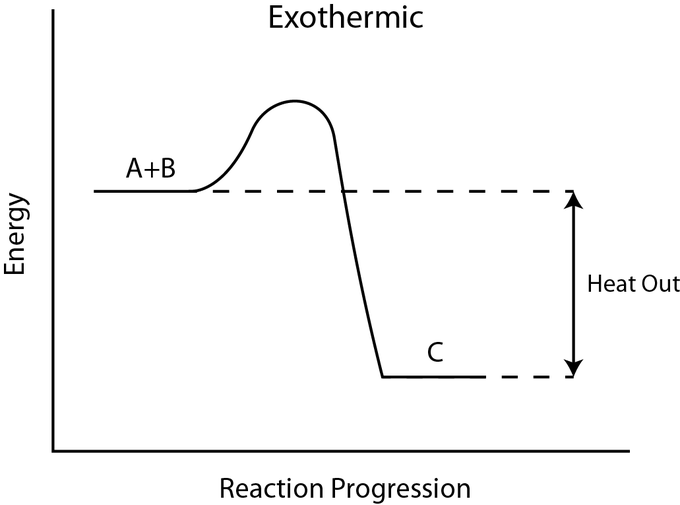
for example
N2(g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
When the medium in which the reaction is taking place collects heat, the reaction is exothermic. When using calorimetry, the total amount of heat that flows into (or through) the calorimeter is the negative of the net change in energy of the system.
The absolute amount of energy in a chemical system is difficult to measure or calculate. The enthalpy, change, ΔH, of a chemical reaction is much easier to work with. The enthalpy change equals the change in the internal energy of the system plus the work needed to change the volume of the system against constant ambient pressure. Bomb calorimetry is very suitable for measuring the energy change, ΔH, of a combustion reaction. Measured and calculated ΔH values are related to bond energies by:
ΔH = (energy used in forming product bonds) − (energy released in breaking reactant bonds)