Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
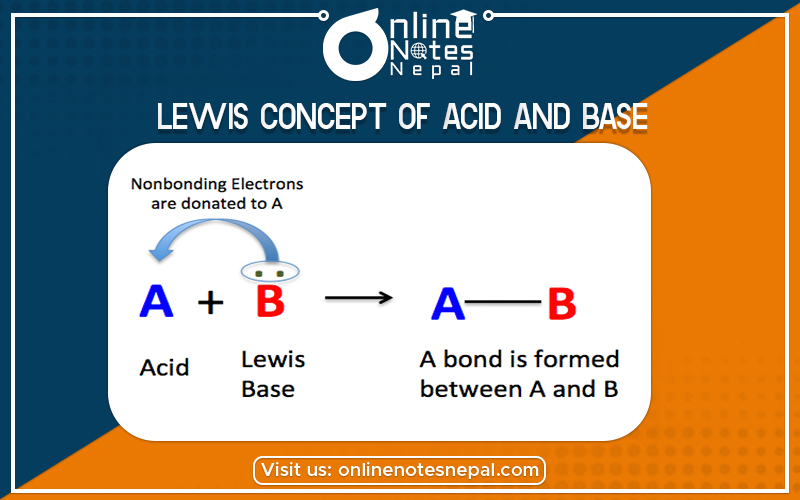
According to Lewis Concept of Acid and Base- the species which can accept pair of electron or electron-pair acceptors are called acids. (Electron pair donor-acceptor system)
According to this concept, the species (charged or uncharged) which can accept pair of electron or electron-pair acceptors are called acids. The species which can donate a pair of electron or electron-pair donors are called bases.
Let us consider the following chemical reaction
H3N: + F3B H3N →BF3
In this reaction, NH3 acts as a base because it donates one pair of electrons, and BF3 acts as an acid because it accepts the pair of electrons. Lewis acids are also called electrophile or electrophilic reagents. Some examples are CL–, Br–, H2O, NH3, etc.
Advantages:-
Limitations of the Lewis concept of acid and base:-
HCL + NaOH → Na+CL– + H2O
(acid) (base)
An acid-base reaction is spontaneous and occurs rapidly but many lewis acid-base reactions are very slow.