Published by: Nuru
Published date: 22 Jun 2021
A multiplexer is a combinational circuit that selects binary information from one of many input lines and directs it to a single output line. It is also called as a data selector since it selects one of many inputs at a time and directs it to the output. The selection of a particular input line is controlled by a set of
selection lines.
Normally, there are 2n input lines and n selection lines whose bit combinations determine which input is selected.
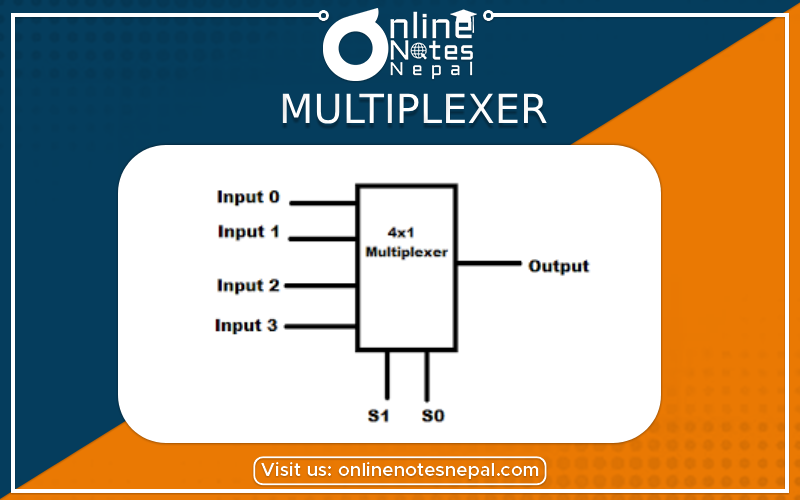
4x1 Multiplexer has four data inputs I3, I2, I1 & I0, two selection lines s1 & s0, and one output Y.
pic
Fig: Block diagram of 4 to 1 line multiplexer
One of these 4 inputs will be connected to the output based on the combination of inputs present at these two selection lines.
Truth table
pic
From Truth table, we can directly write the Boolean function for output, Y as
Y=S1′S0′I0+S1′S0I1+S1S0′I2+S1S0I3
Logic Diagram
We can implement this Boolean function using Inverters, AND gates & OR gate.
pic
To demonstrate the above circuit,
Q. Show how 4-to-1 multiplexer can be obtained using 2-to-1.
Solution:
Logic equation for 2-to-1 MUX Y= s'I0 + sI1
The logic equation for 4-to-1 MUX Y=S1′S0′I0+S1′S0I1+S1S0′I2+S1S0I3
pic
For the combination of a selection input, the data line is connected to the output line. The 8-to-1 multiplexer requires 8 AND gates, one OR gate, and 3 selection lines. As an input, the combination of selection inputs is giving to the AND gate with the corresponding input data lines.
In a similar fashion, all the AND gates are given connection. In this 8*1 multiplexer, for any selection line input, one AND gate gives a value of 1. The remaining all AND gates give 0. And, finally, by using OR gate, all the AND gates are added; and, this will be equal to the selected value.
pic