Published by: Nuru
Published date: 22 Jun 2021
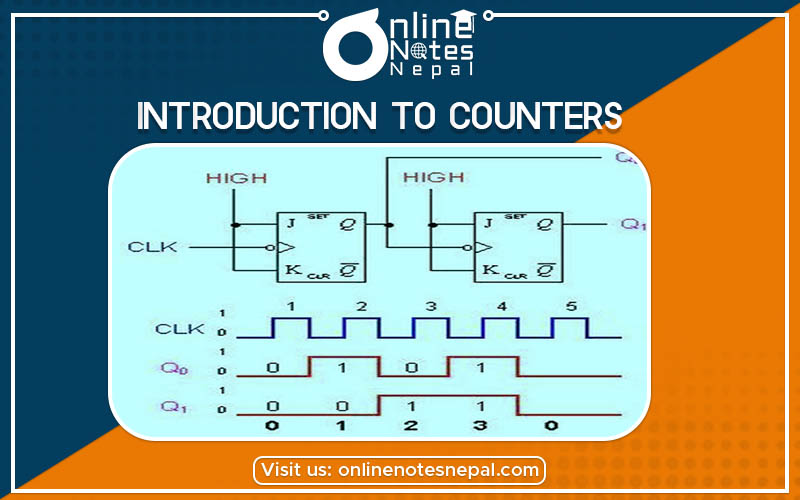
As for the introduction to counters, we say that the counters are the sequential machine that produces a specific count sequence in a circuit. A Counter is a device that stores data and sometimes displays when needed, the number of times a particular event or process, often in relationship to a clock signal. The count changes whenever the input on the clock signal is declared.
A counter can be constructed using the synchronous circuit as well as using the asynchronous circuit. In synchronous, there is the counting of all bits in a synchronous manner, i.e. a regular and stable time interval of the clock signal. And on the other hand, in asynchronous, there are counting of bits in the change of the time interval. A counter can be the UP counter or DOWN counter relying on the input.
The count sequence is due to the limited word lengths. For an n-bit counter, the count is [0, 2n – 1]. This count sequence repeats itself. While counting up, the count sequence goes like 0, 1, 2.…… 2n -2, 2n-1, 0,1 …etc. And in the down counter, it becomes, 2n-1, 2n -2…….2, 1, 0, 2n-1, 2n -2,….etc.
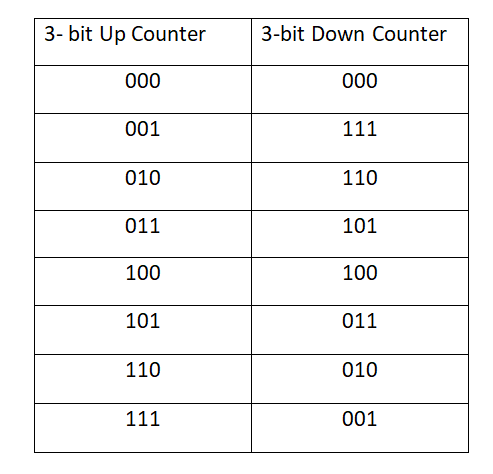
The count sequence for a 3- bit up /down counter is:
If you speak about the complement of the count sequences, they are in the exact reverse order. Below is the same operation for 3- bit Counter :
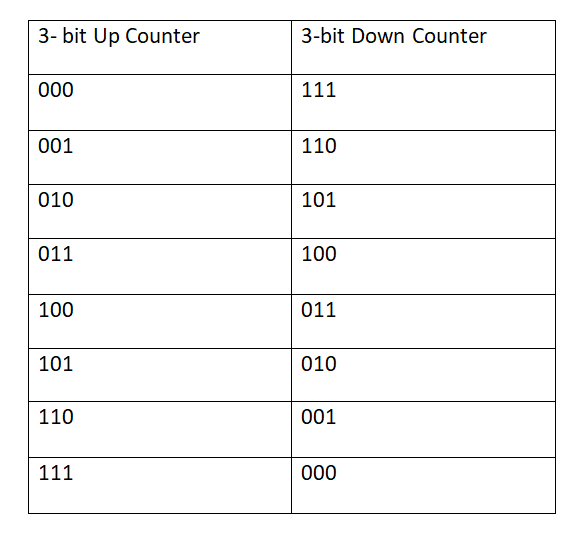
When the assigned possible combinations of the bits repeat itself, then there is a better count sequence.
Counters are classified on the basis of their clock sequence. They are of two types:
The count sequence occurs in the regular time interval. In synchronous counters, the clock output is connected to all of the flip-flops to be clocked. The common pulse triggers all the flip-flops simultaneously, rather than one at a time in succession as in an asynchronous counter.
Another name given to them is ripple counters. The count sequence occurs in irregular time intervals. The sequences of events do not have a relationship between them. In asynchronous, the first flip flop is clocked by the external clock pulse and each successive one is clocked by the next flip-flops. Here, the flip-flop output transition serves as a source for triggering of other flip-flops.
| Synchronous Counters | Asynchronous Counters |
| All the flip-flops are connected in a circuit to be triggered by a common clock pulse. | The external input pulse triggers only the first flip-flop. |
| Speed is high because the clock pulse has the same time for all flip-flops. | The speed is slow as the clock has to go through many stages. |
| It requires more logic gates for its design. | There is a requirement of fewer logic gates. |
| They are faster in the operation. | The ripple counters are slower in operation. |
| It is expensive. | They have a low cost. |
| Standard logic packages are available. | Standard logic packages are not available. |