Published by: Nuru
Published date: 22 Jun 2021
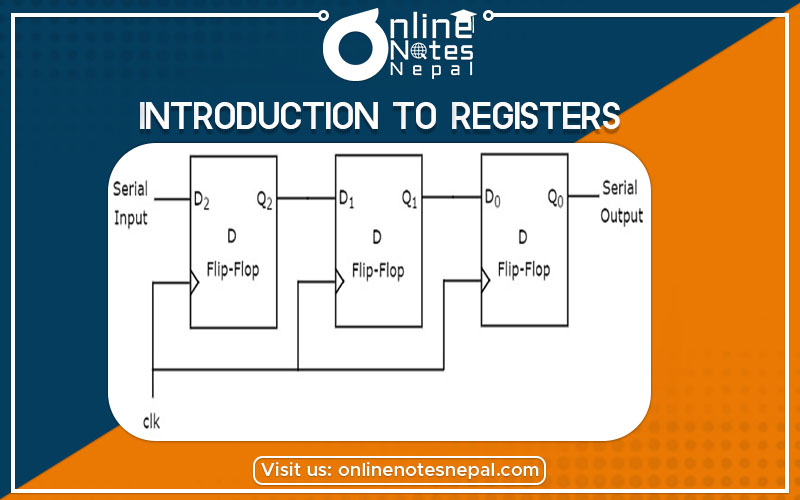
As for the introduction to registers, they are the memory elements inside the computers used for the storage and transfer of digital data and instructions. We make registers by putting many flip-flops together. Registers should be of enough storage for storing instructions. In essence, if the computer is 32 bit, then the registers should be used at 32 bit.
The storage capacity of a register is the total number of bits of digital data it can hold. Each flip-flop in a shift register represents one bit of storage capacity. Therefore, the number of stages in a register determines the register’s storage capacity.
Shift registers are the type of sequential logic circuits for storing data. They are made by a group of flip-flops connected end to end in a chain so that the output of one flip-flop is the input of the other. We can drive all flip-flops by a common clock. The flip-flops in the shift registers are on set or reset simultaneously. It allows storing the information in the adjacent flip-flop because of the adjacent connections.
Shift registers are the digital memory circuits. We can find them in calculators, computers, and data processing systems. They can have both parallel and serial inputs and outputs.
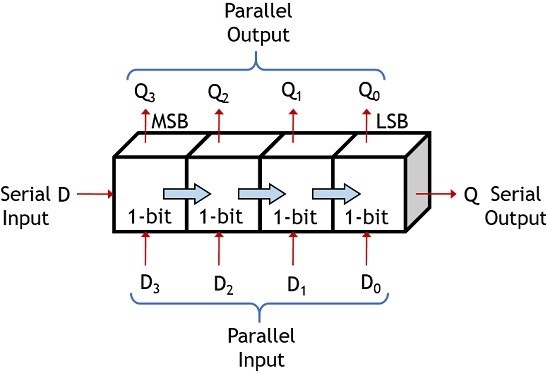
Fig: A Shift Register