Published by: Nuru
Published date: 22 Jun 2021
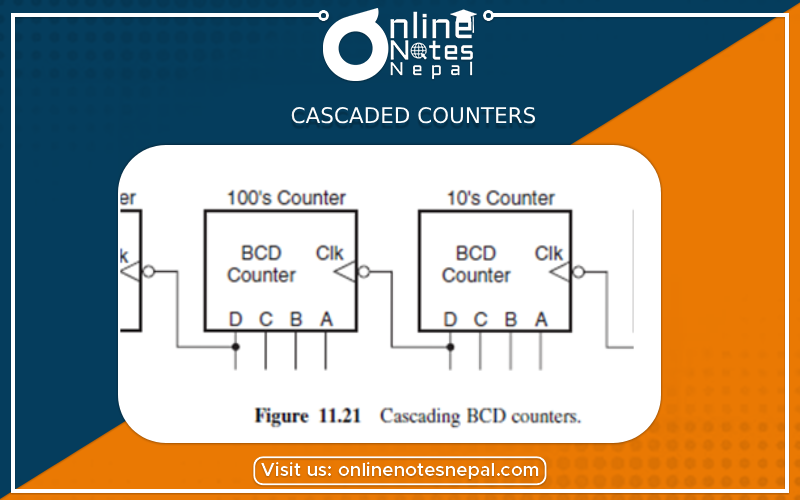
Cascaded counters are those counters which are made up of cascading or grouping of small counters together to the larger ones. Doing this helps in the increasing of both the modulus of the count sequence and also in the frequency division. The making of these types of counters includes digital time clocks, frequency dividers, and also synchronization circuits. In this type of counters, there is the use of rollover signals to communicate when the upper counters should roll over. The cascaded counter will increment only when the counter below it is at its terminal count and it is also increasing.
Cascaded Counter can be either synchronous or asynchronous counters. Let us take the example of the asynchronous counter. The individual toggle stages of the flip-flops of the asynchronous counters are MOD-2 counters. These are cascaded by routing the output of the one-stage into the clock input of the next stage. With each of the deluged stages, the modulus of the counter increases. The final one is equal to that of the modulus of the individual stages of the counter. These underwent multiplication earlier for cascading. A 4-Bit asynchronous counter has a modulus of 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16.
pic
The figure above illustrates the cascaded counter which we call the mod-640 counter. It has the connection in a cascaded form and counts total states of 8 x 8 x 10. In the figure above we see 2 mod-8 counters and a mod-10 counter connected to each other. There is the provision of the clock pulse to the first flip-flop. This has a connection to the input of the second flip-flop, and the output of the second flip-flop has a connection to the clock of the third flip-flop. We see the same process up to the 9th flip-flop.
There is another example of a mod-156 asynchronous counter. The process of the interconnection is as same as the above one.