Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
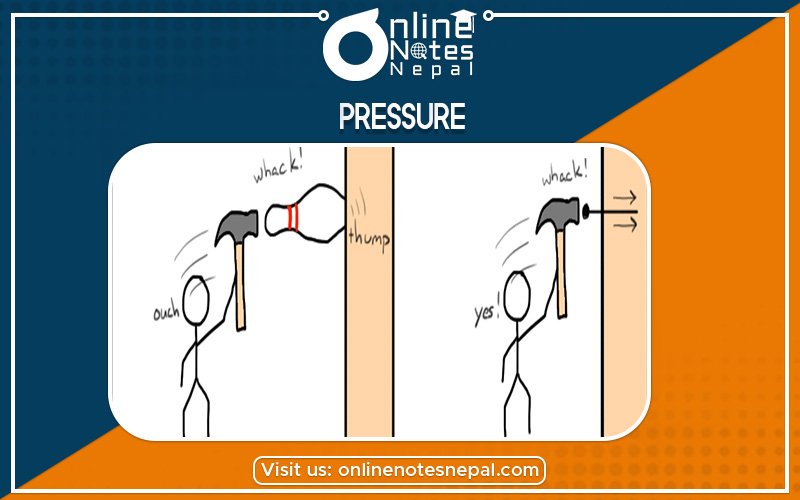
The pressure is defined as the force acting per unit area surface.
Pressure = force/ area =F/A……1
S.I unit is Nm-2 is also called 1Pascal (Pa). The pressure is a scalar quantity.
It is inversely proportional to the area. i.e. force acting on the small area exerts more pressure.
It is directly proportional to the applied force. i.e. more pressure is exerted if the force is increased and vice-versa.

The pressure exerted by the liquid in a vessel is called liquid pressure. Consider a liquid with density d in a beaker of cross-sectional area A and the height of the liquid column is h.
P=F/A
P=m g/A
P=d Vg/A
P=d A hg /A
P=d h g……..1
The factors affecting the liquid pressure are:
The density of the liquid
Depth of liquid
Acceleration due to the gravity
Consequences of liquid pressure:
The pressure exerted by a liquid increases with depth.
A liquid finds its own level
The pressure at any point in a liquid acts in all directions.
Pascal’s Law: Pascal’s law of liquid pressure states that “The pressure is equally exerted perpendicularly on all sides as pressure is applied on a liquid kept in a closed container.”
Instruments based on Pascal’s Law are Hydraulic Brake and Pistons.
Upthrust: Upthrust is defined as the resultant thrust that a liquid uses to push up a body immersed in the liquid. Its SI unit is Newton.
Density: The density of the substance is defined as the mass per unit volume of that substance.
Density (d) = mass/volume
Density is measured in kg/m3 .in S.I system. And In the c.g.s system, it is measured in g/cm3.
Relative density: The ratio of the density of the substance to the density of the substance at 40C is called relative density of the substance. It is unitless.
It states that” When a body is partially or wholly immersed in a liquid, it experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by it.” This principle is used to calculate the upthrust or apparent weight of an object.

Let us consider a cylinder of height h and cross-sectional area A completely immersed in a liquid as shown in the figure.
The top face be at a height of h1 and the bottom face be at a height of h2
Thrust acted on the upper face of the cylinder due to liquid = pressure *area
F1= p1*A
F1 =dgh1 *A …………………1
Similarly, upthrust acting on the bottom face F2 = p2*A
F2 =dgh2 * A
Total upthrust acting on the body = F2 – F1
U = dgh2 * A – dgh1 *A U = d g A(h2 – h1)
U = dgV
So the upthrust of the body immersed in a liquid is directly
The density of the liquid
Acceleration due to o gravity
The volume of the liquid
Also, the weight of the liquid displaced = dgV, which is equal to the upthrust acting on the body.
The Law of floatation states that "The weight of the floating body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the body."
The density of a liquid is directly proportional to the floatation of the object. It means that if the density of the liquid is more than the object, then the object floats whereas if the density of the liquid is less than that of the object, then the object will sink. A hydrometer is a device that is based on the principle of flotation and used to measure the specific gravity and density of liquids.