Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
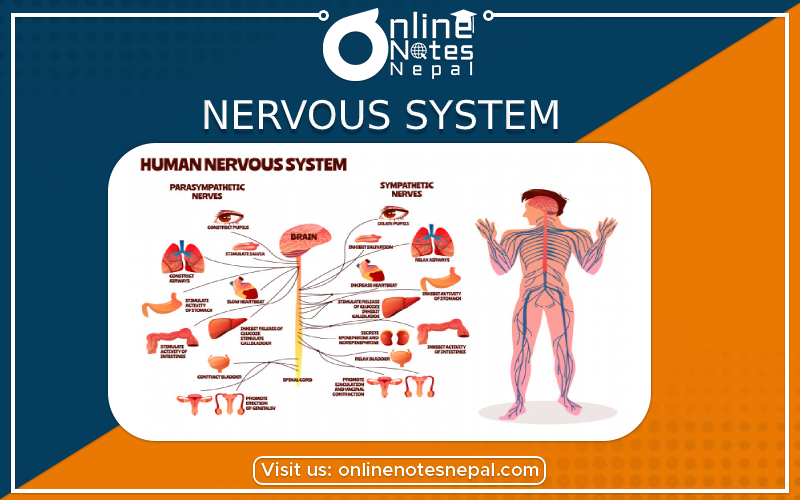
The system which is responsible for controlling other systems of the human body is called the nervous system. There are three major parts of the nervous system.
The major parts of the nervous system are:

Stimulus
The change in the environment or environmental factors into which the organization responds and reacts is called stimulus.
Reaction
The response is shown on an organism towards or away from the stimulus is called reaction. The reaction to the stimulus is a characteristical property of the living organism.
For example, mosquito moves away from a burning mat (chemical).
It means "the burning mat (chemical) brings about change in the environment which is stimulus and the movement shown by the mosquitoes away from the burning mat is the reaction.
Q. Animals respond quickly to a stimulus but plants cannot, why?
Animals use both the nervous system and the endocrine system. So, they can respond quickly to a stimulus but the nervous system is absent in plants and they have only an endocrine system for co-ordination. Therefore, animals can respond quickly to a stimulus but plants cannot.
The biggest and the uppermost part of the central nervous system in the brain.
The brain remains safe inside the cranium of the head. Like the brain, the spinal cord is also made up of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. This liquid protects the brain and spinal cord from external injury.
The brain is completely covered by three membranes known as meninges.
They are:
Cerebrospinal Fluid
The fluid present in between Pia mater and arachnoid is cerebrospinal fluid. This liquid protects the brain and spinal cord from external injury and transmits the impulses towards and away from the brain.
Functions of Brain

The brain is differentiated into three types, they are:
It is the largest portion of the brain which forms about two-thirds of the human brain or 80% of the brain. It is spread in the frontal-parietal and occipital of the cranium. It is divided into two parts as right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Functions of Cerebrum
It is situated just below the posterior portion of the cerebrum. There are two lemon-sized semicircular structures just below the posterior portion of the cerebrum above the medulla oblongata. These are called the cerebellum.
Functions of Cerebellum
It is the posterior part of the brain. It is a cylindrical shape and lies above the spinal cord.
Functions of Medulla Oblongata
Spinal Cord is a long nerve tissue found inside the vertebral column. It starts below the medulla oblongata to the first lumbar vertebra.
Any shock or injuries to the spinal cord due to any disease or accident can cause paralysis of the body parts below the point of injury. Likewise, nerve tissues cannot transfer any message to the brain from the affected parts.
Functions of Spinal Cord
It acts as the path for the transmission of messages from the brain to different parts of the body.
Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves and their branches are produced from the spinal cord which is distributed to the different parts of the body is called spinal nerves.
The longest branch of the nerve cells is called an axon. The several small nerve fibers arising from axons are called dendrites. The nerve cell containing axon and dendrites called neuron combination of axons of nerve cells from nerve fibers.
There are two types of Nerve fibers. They are:
Nerve Cell is known as Neurone. It is the largest cell in the nervous systems. It consists of basically dendrites and axons. 12 pairs originated from the brain are called cranial nerves.

Nerve tissues play the role of a reporter for the spinal cord or the brain. The outer portion of the big brain and inner portion of the spinal cord contains grey matter which mainly comprises of nerve cells of a neuron.
Ganglion
The group of nerve tissues made up of grey matter present near the spinal cord is called a ganglion. They communicate with the spinal cord and brain.
Difference between axon and dendrites:
| Axon |
Dendrites |
| 1. It is the longest branch of the nerve cells. | 1. It is the small nerve fibers arising from the axon. |
| 2. It carries impulses away from the cell body. | 1. It carries impulses towards the cell body. |
Immediate and involuntary action of the body in response to certain stimuli is called reflex action.
For example, we immediately withdraw our hands if we suddenly touch a hot body, blinking of an eye occurs to check the entry of foreign particles, hands immediately support our body when we fall.

Fig: Reflex Action[/caption]
When our fingers touch a hot object, nerves of the finger carry impulses to the spinal cord. Automatically we pull our fingers away from hot objects because of the orders from the spinal cord to our fingers.
The specific way of the nervous systems through which impulses or messages of reflex action transmit is called the reflex arc.
In case of touch of hot object transmission of impulse takes place as follows: