Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
Cell: It is the fundamental structure and functional unit of life. Somatic cells are the cells responsible for the growth and development of human beings.
Chromosome: The thread-like structure present in the nucleus of the cell. The number of chromosomes in the cell of every organism always remains in pairs. But the number differs from one organism to another. Example: frog- 13 pairs, rat-20 pairs, human beings- 23 pairs.
Functions: To transport the parental characteristics to the off-springs.
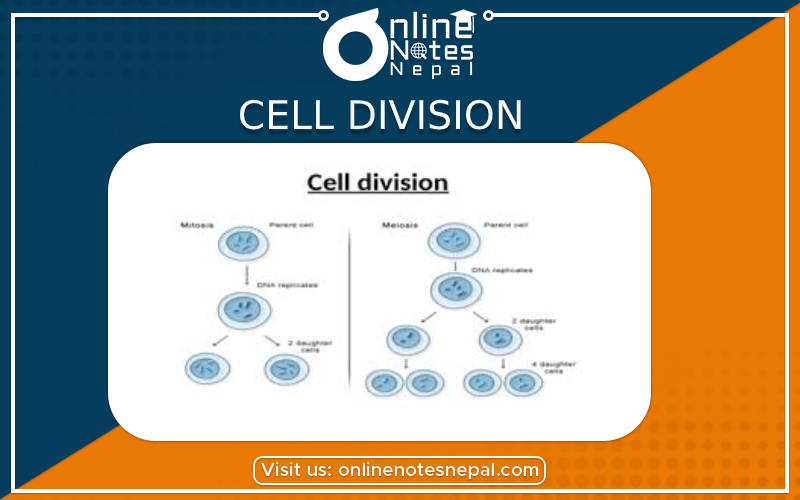
The process of dividing a full-grown cell into two or more two daughter cells. There are two types, they are:
The process in which a mother cell divides into two daughter cells having the number of chromosomes equal to that of the mother cell.
It occurs in somatic cells so it is also called somatic cell division.
In this, a mother cell divides to form two daughter cells. The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is equal to that of the mother cell. So, it is also called the equational division.

The process in which a mother cell divides to form four daughter cells having the number of chromosomes half of that of the mother cell. It occurs in reproductive cells.
In this, a mother cell divides to form four daughter cells. The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is half that of the mother cell. So, it is also called reduction division.

It is the stage just before the division starts. All metabolic activities except the division process occur in this stage. Nucleus, nuclear membrane, and nucleolus are distinct at the interface.
The chromosome is long, coiled, and thread-like which are called chromatins.
