Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
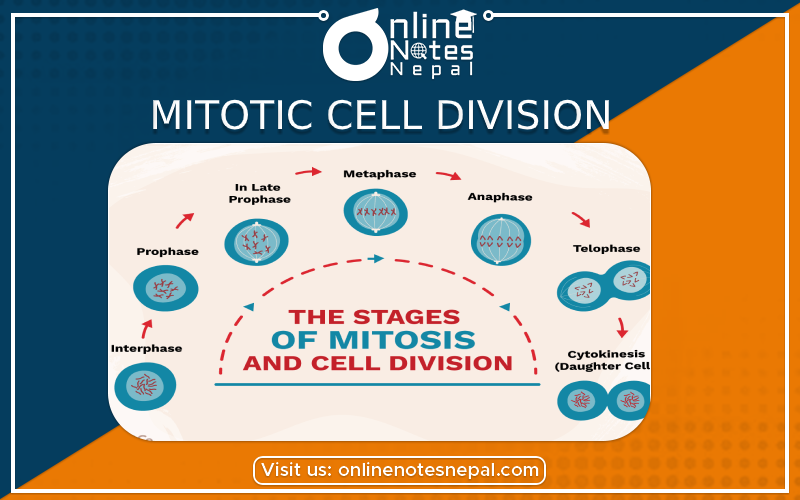
The process in which a mother cell divides into two daughter cells having the number of chromosomes equal to that of the mother cell is called mitotic cell division.
In this, a mother cell divides to form two daughter cells having the number of chromosomes equal to that of the mother cell. In this cell division, the number of genes remains the same and the DNA & RNA contains are also balanced. Thus, each daughter cell has genetic uniformity with the mother cell. As a result, mitotic cell division brings genetic stability to living organisms.
If this cell division becomes uncontrolled it causes cancer.
Mitotic cell division completes into four stages. They are:

Characteristics

Characteristics

Characteristics

Characteristics
Karyokinesis
The division of the chromosome is called karyokinesis.
Cytokinesis
The division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis occurs at the end of anaphase and telophase. In a plant cell, a cell plate is formed in the middle of a cell during cytokinesis. In an animal cell, a constriction is formed from the edge to the center. This constriction is also called cleavage.