Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021

Compounds and its compounds carbon are defined as chemical substances containing carbon. More compounds of carbon exist than any other chemical element except for hydrogen. Organic carbon compounds are far more numerous than inorganic carbon compounds. In general bonds of carbon with other elements are covalent bonds.
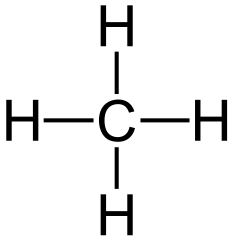
Methane is a colourless, odourless, flammable gas that is the simplest hydrocarbon. It is the major constituent of natural gas and is released during the decomposition of plant or other organic compounds, as in marshes and coal mines. Methane is the first member of the alkane series.
Molecular formula: CH4
Structural formula:
The five uses of Methane are:
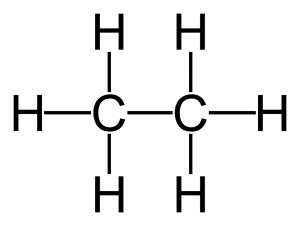
Ethane has many uses. It is the second most abundant component of natural gas that is commonly used in many homes. It is also used to produce a chemical called ethylene, which is a chemical needed in manufacturing products like plastic, automotive antifreeze, and detergent.
Molecular formula: C 2H6
Structural formula:
In chemistry, alcohol is an organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group (−OH) bound to a saturated carbon atom. Organic compounds containing the hydroxyl group attached to saturated carbon atoms or hydrocarbon radicals are known as alcohol.
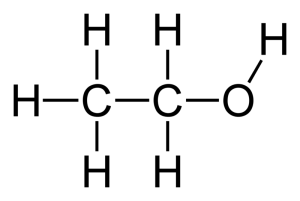
Ethyl –alcohol (C2H5OH)
Structural formula:
Preparation
By oxidation of glucose in the presence of yeast
C 2H12O6→ C2H5OH + 2CO2
Physical properties of alcohol
The uses of alcohol are as follows:
A sweet, syrupy liquid obtained from animal fats and oils or by the fermentation of glucose. It is used as a solvent, sweetener, and antifreeze and in making explosives and soaps. Glycerol consists of a propane molecule attached to three hydroxyls (OH) groups. Also called glycerin, glycerine. Chemical formula: C3H8O3.
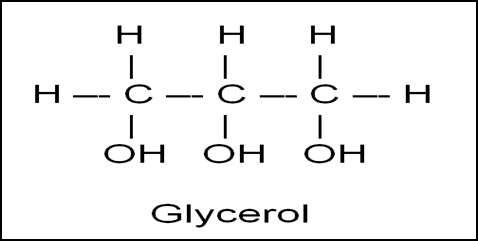
Physical properties
The uses of glycerol are as follows:
Diethyl ether is a colourless, highly volatile flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anaesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication.
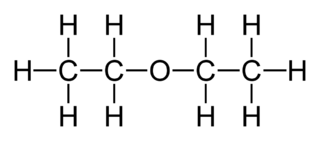
Preparation: By heating the ethyl alcohol in the presence of conc. H2SO4 at 2700C
2C2H5 OH C2H5 –O - C2H5 + H2O
The physical properties of ether are:
The uses of ether are: