Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
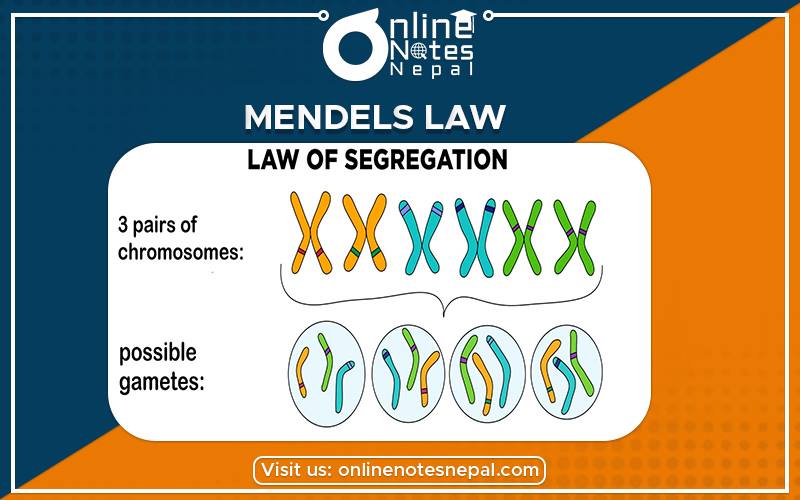
There are three Mendel's Law, they are Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation of Gametes or Law of Purity of Gametes, and Law of Independent Assortment.
It states that "When the cross is made between two parents with one pair of pure contrasting characters, the hybrid is obtained. Hybrid shows the character of one of the parents phenotypically while the character of another parent remains hidden in the hybrid."
Example: When tall and dwarf pea plants are crossed in first-generation all plants are tall.
It states that " Hybrid obtained as a result of a cross between two parents with one pair of pure contrasting characters contain the factor called gene for both contrasting characters. They remain together for a long time in a hybrid and segregate during gamete formation so that 50% gamete receives the gene for dominant character and remaining 50% gamete receives the gene for the recessive character."
Example: When hybrid tall pea are self-pollinated then both pure tall and dwarf are produced in F2 generation it is because of segregation of gamete.
It states that " When two parents differ from each other in two or more pairs of contrasting characters or factors then the inheritance of one pair of factors is independent to that of other pair of factors."
Example: When the cross is made between tall red and dwarf white then tall red, tall white, dwarf red, and dwarf white are produced.
Certain hereditary characters found in human beings also depend on sex. Due to this, certain diseases are seen only in males and while others are seen only in females. Such diseases are called sex-linked diseases.
Example: Baldness can be seen only in males and breast cancer can be seen only in females.
They are macromolecules that are hereditary determinants of living organisms. There are two types are:
Gene is formed by a type of chemical substance deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It is double-stranded in structure. It is composed of a nitrogen base, phosphate, and sugar (deoxyribose).
The nitrogen bases of DNA are of four types, they are:
i. Adenine
ii. Thymine
iii. Guanine
iv. Cytosine
Adenine pairs up with thymine and guanine with cytosine. The difference in the sequence of nitrogen bases may bring about variation in the different organisms and even among the organism of the same species.
It transmits parental characters to their offspring.
It is present in the cytoplasm or nucleolus or chromosome of a cell. It is single-stranded in structure. It is composed of ribose sugar.
The nitrogen bases of RNA are:
i. Adenine
ii. Guanine
iii. Cytosine
iv. Uracil
It takes part in protein synthesis.
The dissimilarities between parents and their offspring are called variations.
The variation of organisms due to hereditary character is called hereditary variation. This type of variation is inherited from one generation to another generation through genes.
The variation brought in the organism due to environmental factors like food, light, temperature, humidity, etc. is called an environmental variation.
The change in the characteristics of the offspring that occur slowly and gradually is known as continuous variation.
The change in the characteristics of the offspring suddenly due to the change in the organism is called a mutation.
The mutation causing factors are Ultraviolet rays, X-rays, Gamma rays, and different chemicals.
Example: A newly born baby without limbs, having an extra finger in hand, one-horned sheep, four-legged chicken, etc.