Published by: Dikshya
Published date: 12 Jul 2023
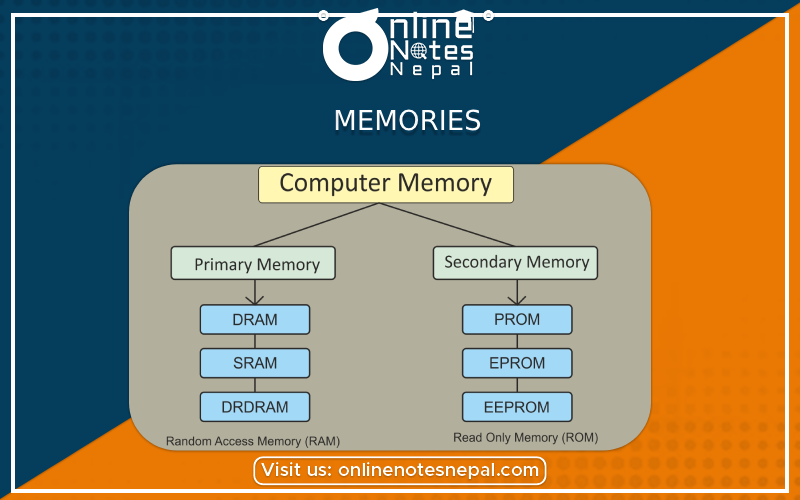
Memories are crucial components in digital systems used for storing and retrieving data. They provide a means of persistent storage, allowing the system to retain information even when power is turned off. Here are some common types of memories:
Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM is a volatile memory that enables read and write operations. It allows data to be stored and retrieved in any order, hence the term "random access." RAM is commonly used as temporary storage for data and program instructions during the operation of a system. It is further categorized into static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM (DRAM), with different characteristics regarding speed, power consumption, and complexity.
Read-Only Memory (ROM): ROM is a non-volatile memory that stores data or program instructions that are permanently programmed during manufacturing. It retains its contents even when power is turned off. ROM is used to store firmware, bootloaders, and other critical system information that needs to be preserved. Examples of ROM types include Mask ROM (MROM), Programmable ROM (PROM), Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM), and Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM).
Flash Memory: Flash memory is a non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It is widely used in various applications such as solid-state drives (SSDs), USB drives, memory cards, and embedded systems. Flash memory offers high storage capacity, fast read and write speeds, and low power consumption. It is organized into blocks and sectors, and data can be written or erased at the sector level.
Cache Memory: Cache memory is a high-speed memory used to improve the overall performance of a system by reducing access times to slower main memory. It stores frequently accessed data or instructions to provide faster access for the CPU. Cache memory is organized into levels, such as L1, L2, and L3 caches, with each level offering different capacities and access speeds.
Magnetic Disk Storage: Magnetic disk storage, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and magnetic tape drives, provides long-term storage for large amounts of data. It operates based on magnetization of the disk's surface, where data is written and read using read/write heads. Magnetic disk storage is commonly used in personal computers, servers, and data centers for persistent data storage.
Optical Storage: Optical storage includes technologies like CDs (Compact Discs), DVDs (Digital Versatile Discs), and Blu-ray discs. These discs use laser technology to read and write data, making them suitable for long-term storage of media files, software, and archival data.
Register Files: Register files are memory components used in processors to store intermediate results, operands, and control information during the execution of instructions. They provide fast access and support simultaneous read and write operations, facilitating efficient data processing in CPUs.