Published by: Dikshya
Published date: 13 Jul 2023
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic), ECL (Emitter-Coupled Logic), I2L (Integrated Injection Logic), PMOS (P-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor), NMOS (N-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor), and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) are different types of logic families used in digital circuit design. Each of these families has its own characteristics, advantages, and applications.
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic): TTL is a popular logic family known for its simplicity and compatibility with a wide range of devices. It uses bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and provides high noise immunity and robustness. TTL circuits have relatively higher power consumption compared to other families but offer fast switching speeds. They are commonly used in applications such as computers, microprocessors, and digital integrated circuits.
ECL (Emitter-Coupled Logic): ECL is a high-speed logic family that uses differential amplifiers and emitter-coupled transistors. It operates at very high frequencies and provides excellent noise immunity. ECL circuits consume relatively higher power but offer very fast switching speeds and high logic density. ECL is commonly used in high-speed applications such as telecommunications, high-performance computing, and radar systems.
I2L (Integrated Injection Logic): I2L is a type of bipolar logic family that utilizes current injection for its operation. It offers low power consumption, good noise immunity, and high-speed performance. I2L circuits are commonly used in applications where power efficiency and high-speed operation are important, such as in digital signal processing and communication systems.
PMOS (P-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): PMOS is a type of MOS logic family that uses P-channel MOS transistors. PMOS circuits operate with positive voltages and have relatively slower switching speeds compared to other families. They are characterized by their simplicity and are commonly used in applications where low-power operation and compatibility with older technologies are required.
NMOS (N-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): NMOS is another type of MOS logic family that uses N-channel MOS transistors. NMOS circuits operate with negative voltages and provide faster switching speeds compared to PMOS. However, they have higher power consumption and are more susceptible to noise. NMOS is used in applications such as microprocessors, memory systems, and digital circuits.
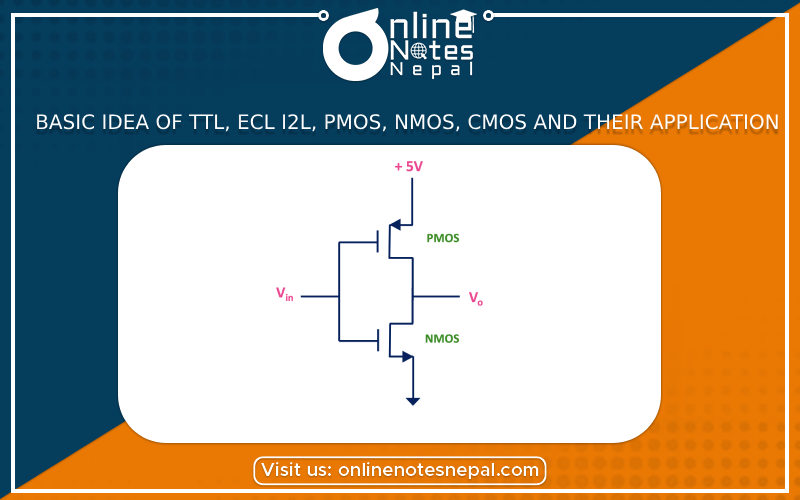
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): CMOS is a widely used logic family that combines both PMOS and NMOS transistors. CMOS circuits provide low power consumption, high noise immunity, and excellent speed-power performance. They are the dominant logic family in modern integrated circuits and are used in a wide range of applications, including microprocessors, digital signal processing, memory systems, and portable devices.
The selection of a logic family depends on factors such as power consumption, speed requirements, noise immunity, voltage levels, and compatibility with existing technologies. Each logic family has its own trade-offs and is suitable for different applications based on these factors.