Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 02 Feb 2022

Solar System The group of eight planets, their satellites and other heavenly bodies including the sun is called solar system. Almost all the masses in the solar system revolve around the sun in their fixed orbit keeping it at the centre. The earth is a planet of our solar system. There are eight planets in our solar system. They are ; Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Besides these eight planets there are other small heavenly bodies like moon, meteors, comet etc in the solar system. All the planets rotate about their axis and revolve around the sun as well. Even the planets do not have their own light, they appear brighter by reflecting the light from the sun.
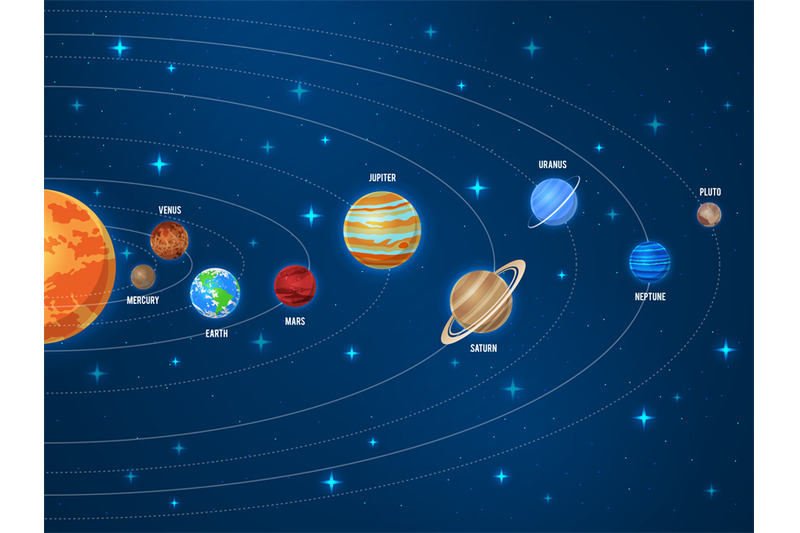

Due to the gravitational force between the sun and the planets they revolve a round the sun maintaining a fixed distance. Out of these eight planets the Mercury is nearest to the sun and the Neptune is farthest to the sun. Jupiter is the largest planet where as the Mercury is the smallest one. Even though almost all the planets look bright, the Venus is the brightest one. On the basis of the closer distance from the sun, the eight planets in the solar system are as follows.
Mercury is the smallest and the nearest planet to the sun. As it lies very nearer to the sun, there is very hot during the day time and very cold during the night time. There is no atmosphere on the Mercury.
The second nearest planet to the sun is Venus. Its size is about similar to the Earth. It is the brightest planet. It can be seen in evening time and early in the morning.
Our home planet where all the requirements for the lives are available is the Earth. Since there is water, atmosphere and suitable temperature for life on the Earth, lives have become possible.
The light red planet in the sky is Mars. Since water and oxygen is found in its atmosphere, it is predicted to have lives in the mars.
The largest planet in the solar system is Jupiter. Till now, the maximum number of satellites are found around this planet.
The planet which looks as big as Jupiter is Saturn. There are three elliptical rings in its outer surface.
Uranus is about 14 times heavier than the earth. It is a very cold planet due to its maximum distance from the sun.
Neptune is the farthest planet to the sun. There is a black spot on it as big as the Earth. All the planets revolve a round the sun in elliptical orbits. The orbits of all the planets lie on the same plane. Some of them are slightly tilted in their orbit. Along with the rotation, all of them have annual motion. The speed rotation (daily motion) and the annual motion (revolution) of each and every planet are different. As the distance from the sun increases, the time period for the rotation of a planet also increases.
Almost all the heavenly bodies are spherical in shape. The sun, the earth and the moon are spherical. Although the moon and the sun look identical in shape and size, the sun looks so due to its longer distance from the earth even it is too much bigger than the moon. As the distance of the objects increases they seem smaller in size. When a big flying kite covers longer distance it is seen to be smaller in size.
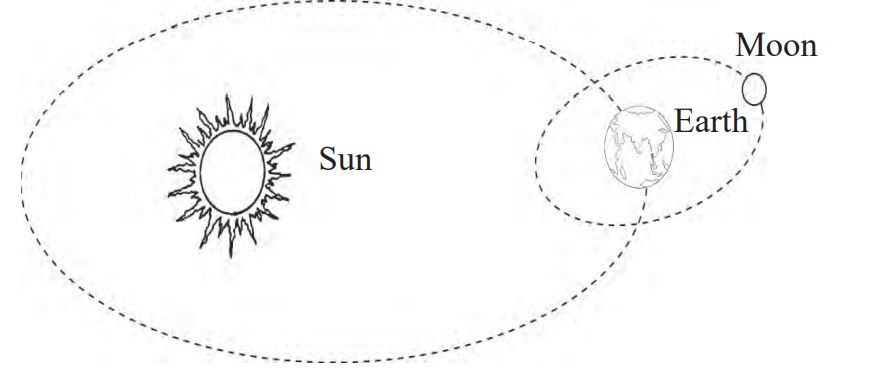
While comparing the size of the moon the sun and the earth, it is necessary to have study about their diameter.
Diameter of the sun: about 1400000 km
Diameter of the earth: about 12751 km
Diameter of the moon: about 3456 km
The given data shows that diameter of the earth is about four times more than that of the moon whereas the sun is 110 times bigger than the earth. We can compare the size of the moon, the earth and the sun by comparing a mustard seed, a pea seed and a football respectively. When the diameter of the earth is taken as 4 cm, the diameter of the moon is to be supposed 1 cm only.
While comparing the distance between the moon, the earth and the sun, the moon is very close to the earth and the sun is very far from the earth.
The distance of the moon from the earth is about 347000 km where as the distance of the sun from the earth is about 150000000 km.
If a marble with diameter 1 cm at a distance of 1 m and 20 cm from a pea seed with diameter 2.5 mm the marble and the pea seed can be considered as the earth and the moon respectively. Similarly if the marble (the earth) kept 430 m apart from a sphere of diameter 1m and 10cm considering it as the sun, the size of the earth and the sun can be compared.
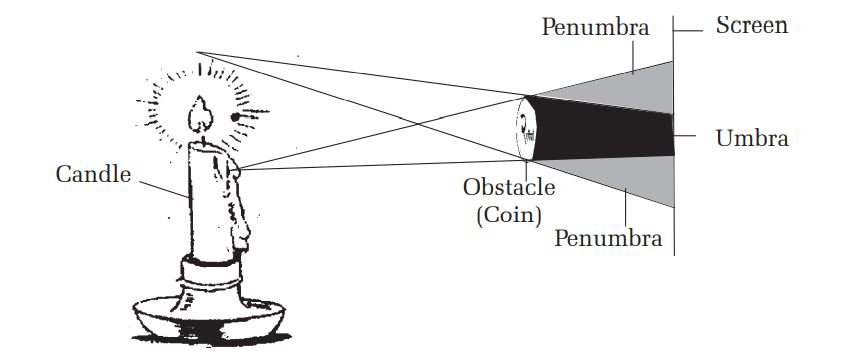
Adjust a white screen and a burning candle at a distance on a table. Now place a 2 rupee coin in between them. The coin should be close to the screen. You will get shadow of the coin casted as the screen. The shadows are of two types on the screen. The shadow at the centre is dark and that at the side is light. The region where the total light is blocked a dark shadow is formed and where the light is blocked partially light shadow is formed. The dark shadow is known as Umbra and the light shadow is known as penumbra.
The moon revolves around the earth and the earth revolves around the sun. Therefore, the moon sometimes comes between the sun and the earth and the earth sometimes comes between the moon and the sun. As a result the shadow may fall on the moon or on the earth. This process of falling of the shadow on a heavenly body is called the eclipse. Mainly there are two types of eclipse, solar eclipse and lunar eclipse. Now we will study about these two types of eclipse.
During the revolution of the earth around the sun and that of the moon around the earth, these three bodies may come in a straight plane being the earth at the middle. In this condition the earth blocks the sunlight for moon.
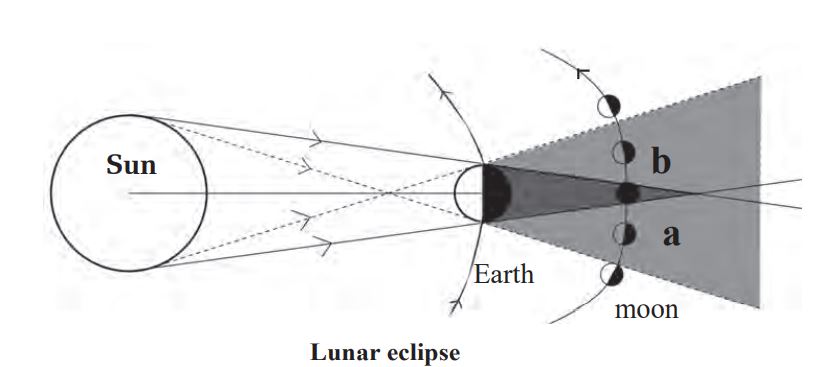
The earth casts its shadow on the moon. If the whole moon lies inside the umbra (figure b) the moon is darkened taotally. This is called total lunar eclipse. If only a certain part of the moon lies inside the umbra (fig a), that part is seen dark. This type of lunar eclipse is called partial lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipse occurs on the full moon.
During the revolution of the earth around the sun or the revolution of the moon aound the earth the three heavenly bodies may come in a straight plane being the moon at the centre. In this condition the moon casts its shadow on the earth. Since the moon is smaller than the earth, it can not block whole earth by casting its shadow. Thus both types of shadow fall on the surface of the earth at the same time. If an doserver is in umbra region he/she observes total solar eclipse. Similarly from the penumbra only a certain part of the sun is seen on the earth. This is known as partial solar eclipse. It occurs in new moon day.
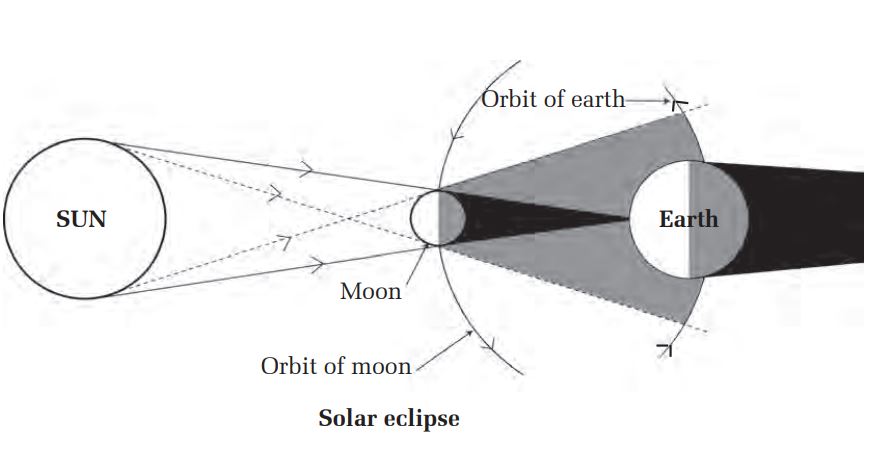
In each new moon and full moon there is a condition of being the sun, the earth and the moon on the same straight line. Since, the orbital plane of the earth and the moon are tilted by certain angle, the eclipse does not occur on each new moon and full moon. Thus the eclipse does not occur on each new moon and full moon.