Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 02 Feb 2022
Structure of body of an organism is made up of cells. A combination of different small bricks makes up a full house. Similarly, animal’s body is made up of combination of one or more cells. Body of animals that cannot be seen with naked eyes like amoeba, bacteria and chlamydomonas is made up of only one cell. Body of multicellular animals is made up of many cells. Animals like earthworm, rabbit, human beings and plants like Sal, Rhododendron and Peepal are some examples of multicellular living beings.
A cell conducts all the life processes like growth, sensitivity, movement, respiration and reproduction, which are very important for animals to survive.
Therefore, cell is the foundation of life of all organisms. Cell is the structural and functional unit of animal organisms. Can you tell what are the constituent elements of fundamental unit cell that make our body?
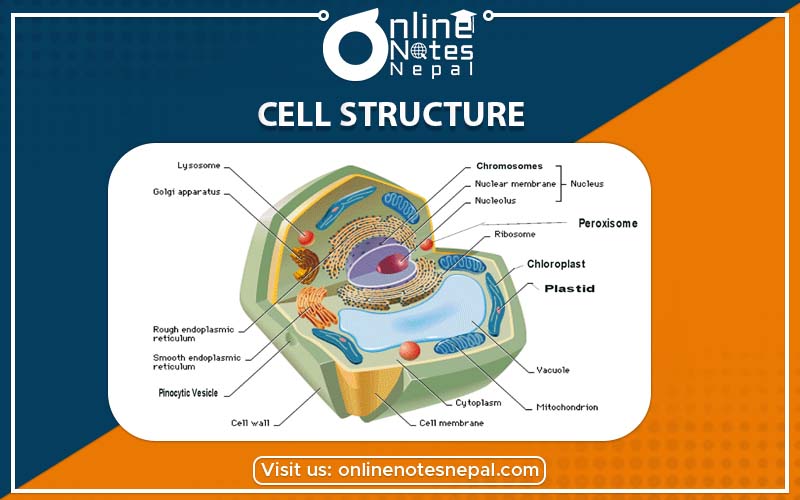
A Combination of different parts makes up a cell. Most of the parts of cells of animals and plants are similar. Function of these parts is also similar. Certain parts of cell are different in plants and animals. Their work is also different. Each cell consists of cell membrane, cytoplasm and vacuole. Apart from these, cell wall, plastid, centrosome, mitochondria, centriole and chromosome are also found in cells. Each of these parts is described below:
Outer part of cell of animals is covered with thin membrane. This is called cell membrane. It is very thin and flexible. It filters important particles and sends them in and out of the cell.
Plant cell consists of a thick and rigid layer lying outside the cell membrane. This is called cell wall. It is made up of cellulose. Cell wall protects and gives fixed shape to the cell.
Cell membrane of animal cell contains of jelly like semi liquid substance, which is called cytoplasm. It contains all the chemicals, which are needed to perform different functions and keeps the cell alive. Different cell organelles float in cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm consists of one circular or oval shaped dark object, which is called nucleus. It is found in every cell of organism. Substances inside nucleus are thicker than the substances inside cytoplasm. It controls different functions of the cell. It also helps in the transformation of hereditary characters from parents to offspring.
Cytoplasm consists of some parts that look like empty sacs. In fact, these parts are not empty sacs but are filled with transparent liquid substance. These parts are called vacuoles. They control the amount of water inside the cell.
Plastids are spread in cytoplasm of plant cells. They do the work of providing different colors to plants. Chloroplast, chromoplast and leucoplast are the three types of plastids found in plant cells. Chloroplast contains chlorophyll. It is green in color. It helps in the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is found in stem and leaves of plants. Therefore these parts of plants are green in colour. Chromoplast is found in fruits and flowers whereas leucoplast is found in roots and stem that is below the ground.
Another important organelle found inside the cell is mitochondria. It is granular and cylindrical in shape. Mitochondria are found in cells of all organisms. It plays an important role to run respiration process in animals and also stores energy. Hence, mitochondria is also called power house of cells.
Near the nucleus of animals there is a microscopic cylindrical shaped structure. This is called centrosome. It plays an important role in cell division. Apart from these, cell also contains other parts. We will discuss about those parts in next class.
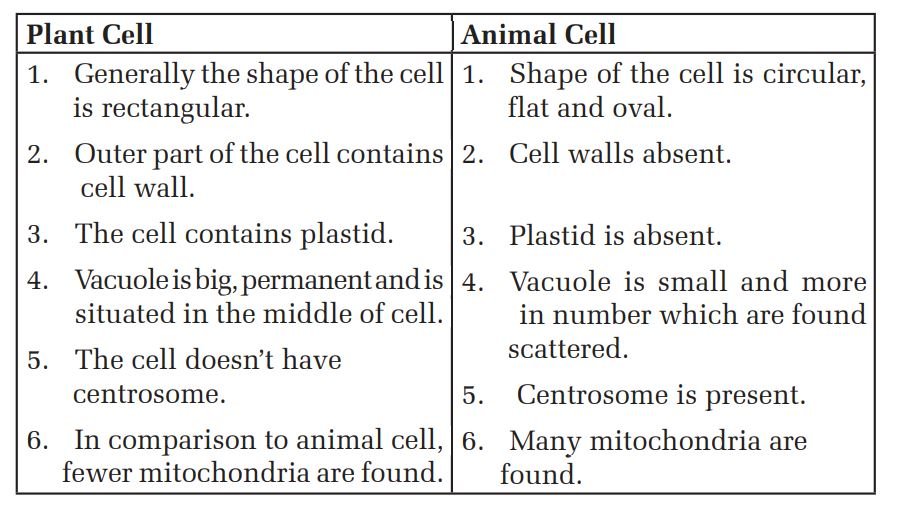
Differences between Plant and Animal Cells:
Bodies of plants and animals are formed of cells. Even though shape and function of both cells are similar, there are certain parts that are unique to either plants or animals. Plant cells have cell wall outside the cell membrane whereas animal cells don’t have it. Even though both plant and animal cells have vacuole, their shape and numbers are different. Plant cells have a big permanent vacuole. It is situated in the middle part of the cell. Vacuoles in animal cells are small, temporary, more in numbers and are found in different parts of cytoplasm. Plant cells have plastids. Hence, roots, stem, leaves, fruits and flowers are of different colors. Animal cell doesn’t have plastid. Thus, we can find various differences between plant and animal cell. Main differences between plant and animal cells are given below:
Plant and animal cell are found in different shape and sizes. Some are long, some are flat and some are rectangular in shape. Generally, cells are tiny and cannot be seen through naked eyes. Some cells are big and can be seen through naked eyes. Ostrich egg is an example of this. Among the cells found in human body, blood cell is the smallest one and neuron is the biggest and longest one. In order to find out the shape and structure of the plant and animal cell, one can study onion cell for plants and cheek cell of human beings for animals.
Bodies of all animals are made of cells. Cells have different parts. Each part has its own distinctive work. Depending on the nature of functions, shapes of cells differ. Different life process that are needed for the animals to live like growth, movement, reproduction, photosynthesis, respiration, transportation etc. are all run by cell. Therefore, animals can only live when cells live. Main functions of the cells are as follow:
a) They construct the body structure of animals.
b) They provide shape to body of animals.
c) They conduct run the life processes.
d) They help to continue generation.
e) They transfer the hereditary characters from parents to their offspring.