Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 02 Feb 2022

For organisms to live, different processes like respiration, transportation, excretion, etc. are run inside their bodies on a regular basis. These processes are called life processes. Different parts of the body take part in running these processes. In this chapter, we will learn about different parts of plants and life processes they perform.
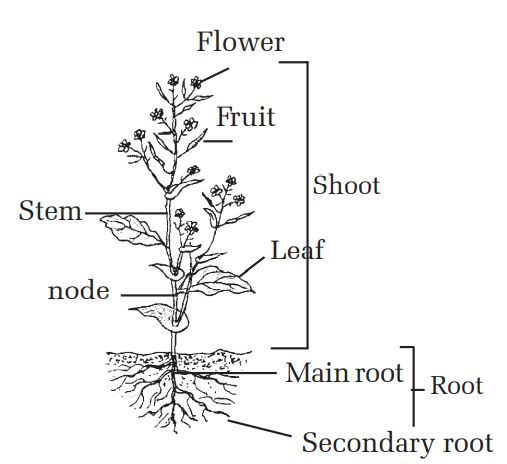
Different types of plants are found in our surrounding. Have you noticed that all the plants sen bear flowers in them. Plants can be divided mainly into two groups: flowering and non flowering plants. Generally, life of all flowering plants starts when seed comes in contact with soil. During seed germination, one part grows above the soil and the other below the soil. Part of the plant above the soil is called shoot and the part below the soil is called root. Shoot contains stem, leaves, fruits and flowers. Roots also have different parts. In this way, a whole plant can be divided into two groups: shoot and root.
Generally, root is the descending portion of the plant. They are usually pale and creamish brown in color. Depending upon the nature of the roots, the roots of plants can be divided into tap root and fibrous root. In tap root, one main root descends down the land. This root is called primary root. Other branches on the lower part of the tap root are called secondary roots. Small hair like structures on the secondary roots are called root hairs. Since the end part of the tap root is very soft, it is covered with cap like thing which is known as root cap. Dicotyledonous plants like mustard, gram, mango, apple etc. have this type of root. In fibrous root, small clusters of roots come out of the lower part of the stem. These roots don’t divide into other small roots. In this type of root, main root, root hairs and root cap aren’t present. Fibrous root is found in monocotyledonous plants like wheat,maize, rice etc.
Roots help plants to stand straight on land. Therefore, plants do not fall down easily. Another important function of root is to absorb water and mineral salt from the land. Roots of plants are spread under the ground like a web. Roots tightly hold the land. Because of this it is hard to pull the plants from the ground. When we pull the plants, it comes with some soil. As plants hold the soil in this way, soil erosion cannot take place in the areas where there are plants. Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil and send it to stem and other parts of plants. Some roots are modified as food storage of plants. We can use these roots as our food. Radish, carrot, sweet potato, sugar beet etc. are some of such examples.
The part of the plant above the ground is called shoot. Stem, leaves, fruits and flowers are parts of shoot.
Stem is a part of the upper part of the plant. The lower part of the stem, which is near the land, is thick and is gradually gets thinner at the top. Generally, the stem is straight and round. It helps the plants to remain straight. Leaves and branches come out of the stem. Part of the stem from where leaves and branches grow is called node. Nodes of stem remain in fixed proportion. Space between two nodes is called internode.
Upper end of the stem contains bud, which is called terminal bud. This helps the plant to grow. In some plants, buds come out from the part where stem and leaves are attached. These types of buds are called auxiliary buds. Some plants have thick and strong stem whereas some have thin and weak stem. Tall trees have thick and strong stem. Plants like pumpkin and cucumber have thin and weak stem.
The main function of stem is to take the water and nutrients that is absorbed by the roots to other parts like fruits and flowers. Also, stem is responsible for taking food prepared by the leaves to other parts of the plant. Two tissues called xylem and phloem, found in stem, perform this work. Xylem transports water and salt whereas phloem transports food. Stem provides support to branch, leaves, fruits and flowers. It spreads the flowers in a way that the leaves can get more sunlight. Stem of some plants are modified into food storage under the ground. Onion, potato, ginger etc. are some of its examples.
Leaves come out of the stem and branches of plants. The way in which the leaves come out of the stem and branches differ depending on the types of plant. Because of the presence of chlorophyll in leaves, it looks green. In some plants yellow, red and violet colored dots can be seen. Therefore leaves have more colors apart from chlorophyll.
Generally, leaves are flat. This part of the leaf is called lamina. End part of some leaves is straight whereas some is cut. Lamina provides shape to the leaves. The part of the leaf that connects lamina to the stem is called petiole. If only one leaf comes out from the petiole, then that leaf is called simple leaf. If more than one leaf comes out from the petiole, then those leaves are called compound leaves. For example: Leaf of mustard plant is simple leaf whereas leaf of gram is compound leaf. From the base of lamina, veins come out and these veins are spread throughout the lamina. The thick vein which lies on the middle part of the lamina is called mid rib. In some leaves, other small veins come out of the mid rib and these are spread around the leaf like a web. This kind of arrangement of the veins is called reticulate venation. In some plants, other veins are spread parallel to the mid rib. This kind of arrangement of the veins is called parallel venation.
The main part of plant that makes food is leave. With the help of chlorophyll and in the presence of sunlight, leaves prepare enough food needed for the plant. That food of the plant is called starch. Since the food of plant made in leaves, leaves are also known as kitchen of the plants. In order to make food of plant, water, carbon-dioxide and sunlight are needed. Leaves of plant contain small pores, which are called stomata. With the help of the stomata, plant performs respiration. During the process of respiration, like animals plants also take in oxygen and throw out carbon-dioxide. With the help of the stomata present in leaves, plant sends the unwanted water to the atmosphere in the form of vapour. In some plants, leaves are modified into thorns, which protect the plant. Cactus is an example of this.
Leaf of the plant is the main part where food is prepared for the plants. Plant's food is prepared in the form of starch. With the help of stomata present in leaves, plant throws out the unwanted water in the process called transpiration.
If we don’t provide water to the potted plants for a long time, the plants will wither or die out. We have heard the news of drought and reduced production of crops time by time. That is why we should know the importance of water for the life of plants. Can you tell where and how do plants get water from?
The roots of the plants spread under the soil like a web. The roots of small plants spread in a lower depth below the land while the roots of bigger plants, different trees spread in a very deep. In this part water and minerals mix in the water. The roots of the plants take in this water and minerals. This process among the plants is called ‘absorption’. In this way the ‘absorption’ process in plants make the water and minerals of soil reach to the roots of the plants. This is a continuous process.
Water and minerals attained from the roots get passed along stem, leaves and other parts. When they reach the leaves, the necessary food and nutrition form which is called ‘starch’ through photosynthesis. The food formed in the leaves pass along stem, fruits, flowers, roots and the plants grow. In this way, water, minerals and nutrition come and go within the plant body in a continuous process. This process in the plants is called ‘transportation’. For the process of transportation, there are xylem and phloem in the stem of the plants. Xylem transports water and minerals taken from the roots to the leaves and phloem transports nutritive elements formed in the leaves to roots and other parts which are responsible for ‘storage’.
Through the process of absorption and transportation there is regular supply of water from the soil to the leaves. Do leaves use all the water they gain? Some part of the water that reaches the leaves is used to make food and some is thrown out to the atmosphere. With the help of the stomata present in leaves, a plant sends the unwanted water to the atmosphere in the form of vapour. This process of sending the water outside in the form of vapour is called transpiration. Since the unwanted water reaches the atmosphere through transpiration process, there is more rainfall in forest areas than other areas and the air is also moist. The amount of water that the plants take in from the soil is the same as the amount of water the plant throws out through the transpiration process.