Published by: Nuru
Published date: 05 Dec 2021
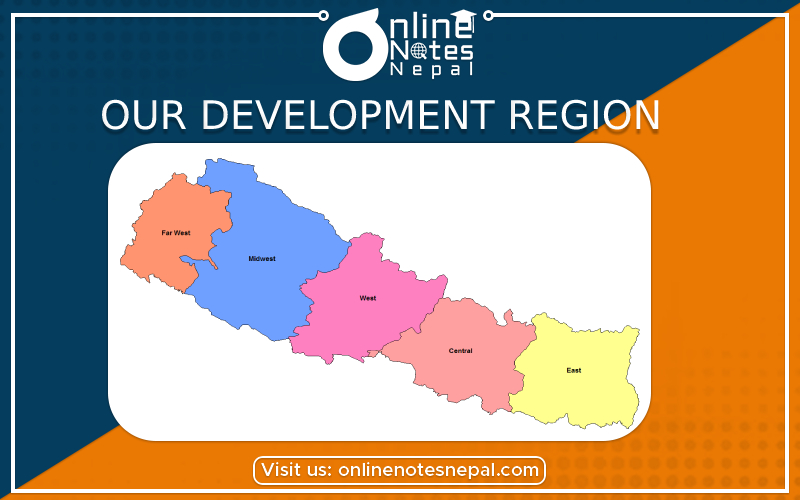
Nepal is divided into five development regions. In this chapter, we discuss about the five development regions of Nepal, advantages of having development region under Grade 8 Social Studies.
To operate the proportional, justiciable and balance development in the country, the concept of development region was derived. Therefore Nepal is divided into five development regions.
Formation of Development Regions
| Name of Development Regions of Nepal | Headquarter | Area | No. of zones | No. of districts | No. of V.D.C. | Areas(km²) |
| Eastern Development Region | Dhankuta | 28,456 km2 (10,986.9 sq mi) | 3 | 16 | 893 | 28,456 |
| Central Development Region | Kathmandu | 27,410 km2 (10,583.1 sq mi) | 3 | 19 | 1199 | 27,410 |
| Western Development Region | Pokhara | 29,398 km2 (11,350.6 sq mi) | 3 | 16 | 864 | 29,398 |
| Mid-western Development Region | Birendranagar | 42,378 km2 (16,362.2 sq mi) | 3 | 15 | 575 | 42,378 |
| Far-western Development Region | Dipayal | 19,539 km2 (7,544.1 sq mi) | 2 | 9 | 383 | 19,539 |
| Total | 1,47,181 km2 | 14 | 75 | 3914 | 147,516 |
Advantages of development regions:
The division of development region in Nepal has great importance. The foremost importance is smoothness and effectiveness in the running of administration, utilization of local resources in a short period, employment opportunities, etc.
Some of the importance of development regions:
Develop the feeling of competition:
The feeling of competition creates rapid development in every region as everyone wants to be more advanced than the others. As a whole, the country develops rapidly.
Utilisation of resources and manpower:
Development regions use the available resources and manpower of its own region because importing the manpower and resources is expensive. Therefore, the resources won't go to a waste and people also get job opportunities.
Proportionate development: Proportionate development occurs in every development regions as there is the facility of health, education, transport, communication, electricity, etc. in all development regions.
Decentralisation of power:
Due to decentralisation of power, public participation increases. As the people want change, they carry out development activities with each others' cooperation.
Promotion of local culture:
Development region helps to know the problems arising in cultures and traditions of the local areas. The problem is understood in local level and effective remedies are applied.
Eastern Development Region:
There are 3 zones in Eastern Development Region, they are Mechi, Koshi, Sagarmatha and 16 districts. Mechi, Koshi, Kankai etc are the major rivers of this development region. Mt. Everest, Kanchanjunga, Makalu, Lhotse, Eumori are the main mountains of this development region.
Sagarmatha National Park, Makalu Barun National Park, Kanchanjunga Conservation Area, etc. are the main parks and areas of this development region. Biratnagar, Dharan, Illam, Bhojpur are the major towns of this development region. Geographically it is divided into Terai, Hilly and Mountain region.
Central Development Region:
It has the Eastern Development region to the east, India to the south, Western Development Region to the west. It is the fourth largest development region of Nepal with an area of 27,410 km2(10,580 sq.m). There are 3 zones, which are Janakpur, Narayani, Bagmati, and 19 districts in this development region.
Rapti, Bhote Koshi, Kamala, Gosaikunda, Mt. Gaurishankar, Chitwan National Park, Shivapuri Wildlife Reserve, Langtang National Park, Parsa Wildlife Reserve, lies in this development region. Its major cities are Kathmandu, Dhulikhel, Janakpur, Hetauda, Patan, Bharatpur, Bhairawa, Lalitpur, Nagarkot etc. Geographically it is also divided into Mountain, Hill and Terai.
Western Development Region:
The Western Development Region is located in the west-central part of the country. Its headquarter is in Pokhara. Lumbini, Dhaulagiri and Gandaki are the 3 zones of this development region.It has 16 districts. Marshyangdi, Lake Fewa, Lake Begnas, Mt. Annapurna, Mt. Dhaulagiri, Manaslu and Thaple pass lies in this development region.
It also has Annapurna Conservation Area, Dhorpatan Hunting Reserves, Makalu Eco-Tourist Centre. Its major places are Pokhara, Bhairawa, Tansen, Lumbini, Muktinath etc. Geographically it also has Terai, Hill and Himalayan regions and has a similar climate like Eastern Development region.
Mid-Western Development Region:
Rapti, Bheri, Karnali, are the three zones of this region. There are 15 districts in this region. Its main rivers are Karnali, Bheri, Rapti, Babai, etc. and mountains are Mt.Kanjiroba, Mt.Sisne, Mt.Patarasi etc. Bardiya National Park, Shey Phoksundo National Park, Rara National Park are some of the conservation areas of this region.
Its major trade centres are Dang, Nepaljung, Birendranagar etc. Its main highways are Ratna Highway and Mahendra Highway. Geographically it also has Hilly, Himalayan and Terai regions. Its total area is 42,378 square km (16,362 sq m). Birendranagar is the headquarter of this region. It occupies 29.2% of the total land of Nepal.
Far-Western Development Region:
There are 2 zones in Far-Western Development Region. They are Seti and Mahakali. There are 9 districts in this region. It is located at the western end of the country. Seti and Mahakali are the two major rivers of this development region.
Mt. Api and Mt. Saipal are the two main mountains of this development region. Suklaphanta Wildlife Reserve, Khaptad National Parks, etc. are the main places which help to attract tourists to this development region. Its major trade areas are Dhangadhi, Mahendranagar and Dipayal. Its main highways are Mahendra highway and Bhimdutta highway. Its area is 19,539 km2 (7,544 sq mi). Dipayal is the headquarter of this region.