Published by: Nuru
Published date: 17 Jun 2021
The method that is used to transfer information between internal storage and external I/O devices is known as the I/O interface. The CPU is interfaced using special communication links by the peripherals connected to any computer system. These communication links are used to resolve the differences between the CPU and peripheral. There exist special hardware components between the CPU and peripherals to supervise and synchronize all the input and output transfers that are called interface units.
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Different from Programmed I/O and Interrupt-Driven I/O, Direct Memory Access is a technique for transferring data within the main memory and external device without passing it through the CPU. DMA is a way to improve processor activity and I/O transfer rate by taking over the job of transferring data from the processor and letting the processor do other tasks. This technique overcomes the drawbacks of the other two I/O techniques which are the time-consuming process when issuing the command for data transfer and tie-up the processor in data transfer while the data processing is neglected. It is more efficient to use the DMA method when a large volume of data has to be transferred. For DMA to be implemented, the processor has to share its’ system bus with the DMA module. Therefore, the DMA module must use the bus only when the processor does not need it, or it must force the processor to suspend operation temporarily. The latter technique is more common to be used and it is referred to as cycle stealing.
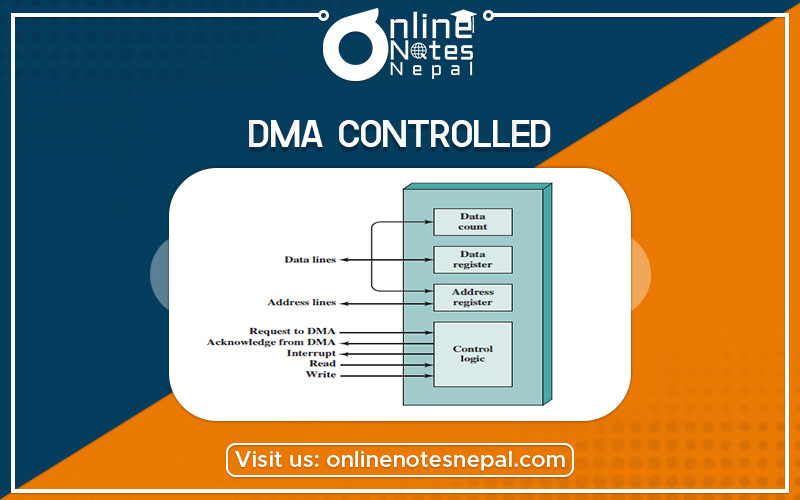
Basic Operation of DMA
When the processor wishes to read or send a block of data, it issues a command to the DMA module by sending some information to the DMA module. The information includes:
Configurations of DMA
DMA mechanism can be configured in a variety of ways, which are: