Published by: Nuru
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
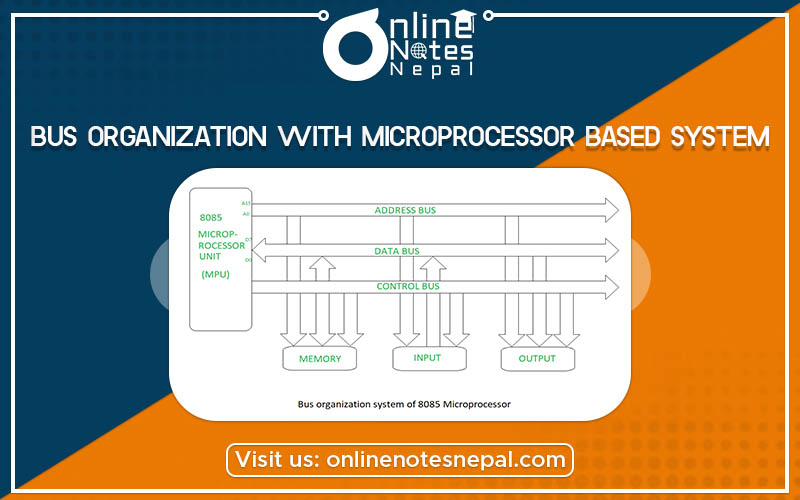
A bus organization is a group of conducting wires which carries information, all the peripherals are connected to a microprocessor through the bus. A system bus is nothing just a group of wires to carry bits.
The MPU (Micro Processing Unit) performs primarily four operations:
The diagram to represent the bus organization of the 8085 microprocessor is given below:-
Types of Bus in the microprocessor are:-
i. Address Bus:-
The address bus carries information about the location of data in the memory. The addresses bus is unidirectional because of data flow in one direction, from the microprocessor to memory or from the microprocessor to input/out devices. The length of the Address bus of 8085 microprocessor is 16 bit (That is, four hexadecimal digits), ranging from 0000H to FFFF H. The microprocessor 8085 can transfer a maximum of 16-bit addresses which means it can address 65,536 different memory locations i.e 64KB memory.
Address Bus is used to perform the first function, identifying a peripheral or a memory location.
ii. Data Bus:-
The data bus allows data to travel between the microprocessor (CPU) and memory (RAM). The data bus is bidirectional because of data flow in both directions, from the microprocessor to memory or input/output devices and from memory or input/output devices to microprocessors. The length of the Databus of 8085 microprocessor is 8 bit (that is, two hexadecimal Digits0, ranging from 00H to FF H.
The data bus is used to perform the second function, transferring binary information.
iii. Control Bus:-
The control bus carries the control signals to control all the associated peripherals, the microprocessor uses control bus to process data, that is what to do with selected memory location signals are:-
a. memory card
b. memory write
c. input/output, write.