Published by: Nuru
Published date: 17 Jun 2021
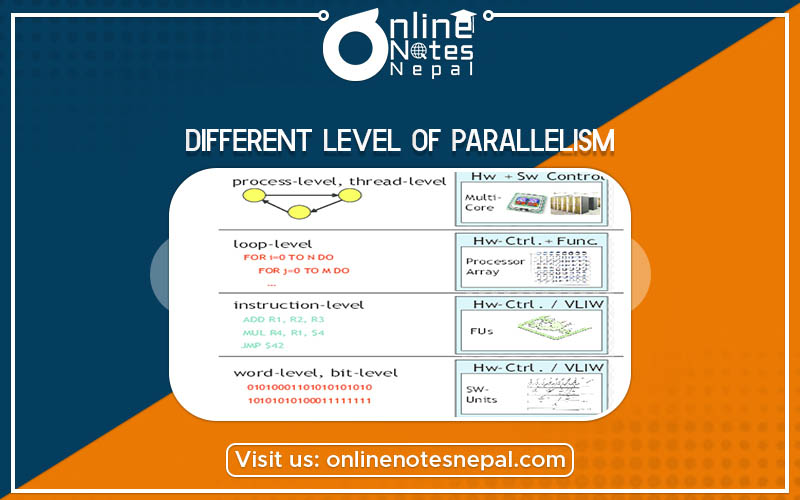
There are several different levels of parallelism: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but it's gaining broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.
Instruction level
Instruction-level parallelism (ILP) is a measure of how many of the instructions in a computer program can be executed simultaneously. ILP must not be confused with concurrency since the first is about parallel execution of a sequence of instructions belonging to a specific thread of execution of a process (that is a running program with its set of resources - for example its address space, a set of registers, its identifiers, its state, program counter, and more). Conversely, concurrency regards with the threads of one or different processes being assigned to a CPU's core in a strict alternate or in true parallelism if there are enough CPU's cores, ideally one core for each runnable thread.
Process Level
A process level is an organizational level defined within the HR company structure. Process levels fall below companies and above departments. A process level can belong to only one company, but it can have multiple departments below it in the HR company structure.
The following list outlines some of the characteristics of process levels:
Thread level parallelism
Thread level parallelism is a software capability that allows high-end programs, such as a database or web application, to work with multiple threads at the same time. Programs that support this ability can do a lot more, even under high levels of workloads. Thread-level parallelism can be controlled to some degree by the execution configuration specified in the host code used to launch kernels. In the execution configuration, we specify the number of threads per block and the number of blocks in the kernel launch. The number of thread blocks that can reside on a multiprocessor for a given kernel is then an important consideration and can be limited by a variety of factors.