Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 19 Jan 2022
Different business activities are carried on by the people generating incomes. On the basis of the nature of these business activities, the business can be classified as follows:
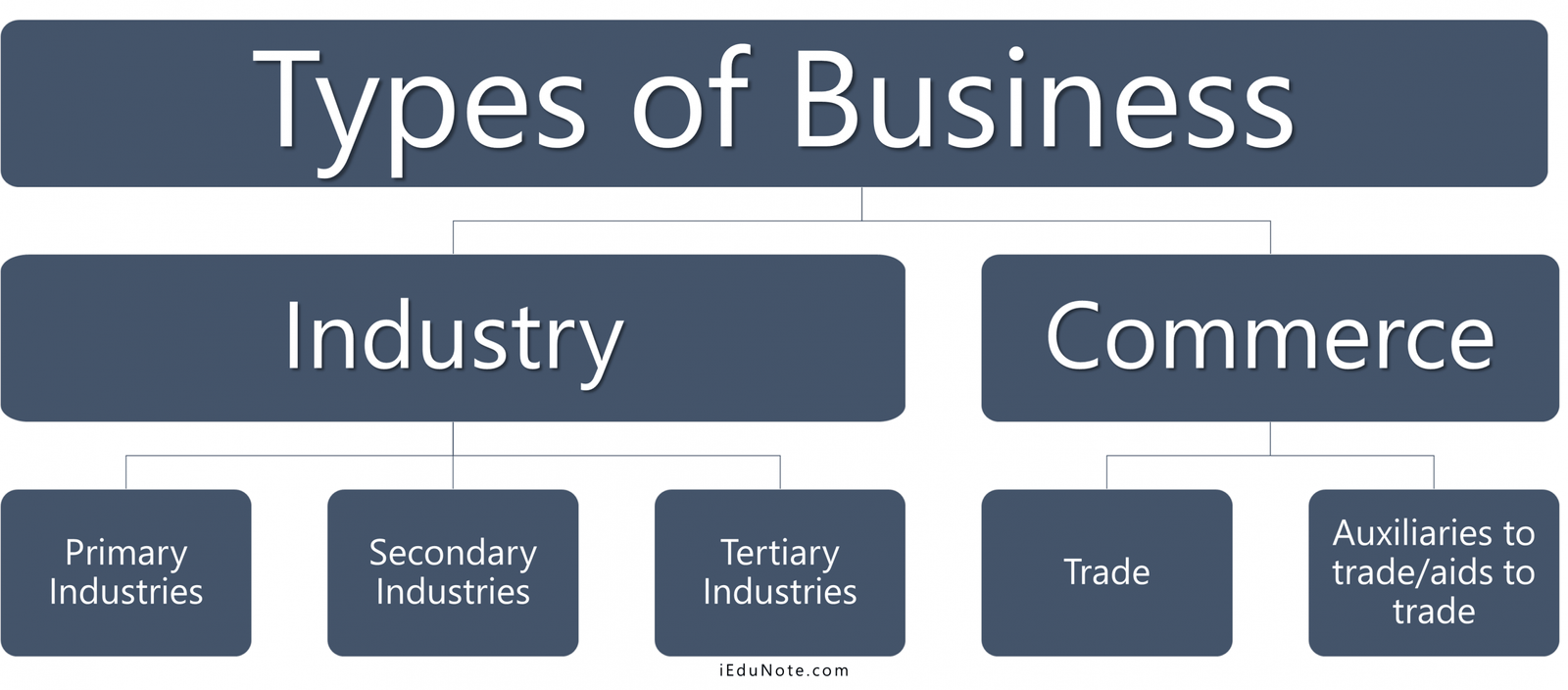
Industry refers to the act of producing raw materials and finished goods. It is the process of converting raw materials into finished goods. It is the activity relating to extraction, reproduction, manufacturing and construction of products. On the basis of production, an industry can be classified as follows:
1. Primary industry: The Primary industry is concerned with extracting raw materials from the soil or beneath the surface of the earth and reproducing certain species of plants and animals. The final products of primary industry are used as raw materials by secondary industry. The primary industry can be divided as follows:
2. Secondary industry: The Secondary industry is concerned with converting raw materials into finished goods and constructing different assets. The final products of secondary industry can be directly consumed by final customers. The secondary industry can be divided as follows:
Commerce refers to the act of buying, selling and distributing of goods and services. It is the process of connecting the producer of goods with their final consumers. It is the activity related to buying, insurance, transportation, warehousing and communication. It can be divided into two classes as follows:
Trade is concerned with buying and selling of goods. It is the process of exchanging goods with money for mutual benefits of the buyer and seller. It is the act of transferring the ownership of goods from the seller to the buyer. It can be classified as follows:
1. Home trade
Home trade is the act of buying and selling goods within the boundary of the country. It can be classified as following:
2. Foreign trade
Foreign trade is the act of buying and selling goods outside the boundary of the country. It is carried on between the citizens of two or more countries. The payment of goods in foreign trade is made in foreign currencies. It can be classified as follows:
In the process of distributing goods to different markets, the seller has to face a number of problems. These problems are related to finance, insurance, transportation, warehousing, and communication. To remove such problems and facilitate for distribution of goods and services, certain organization are established. This organization do not involve in production and distribution of goods but facilitate the distribution of goods and services, certain organizations are established. These organizations does not involve in production and distribution of goods and services. These organizations assists or support in the process of buying and selling to make the distribution effective. Hence, aid to trade refers to the facilities provided by different organizations to remove the problems of distributions. Banking, insurance, transportation, communication, etc. are the examples of aid to trade which facilitate the effective distribution of goods and services.