Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 21 Jan 2022
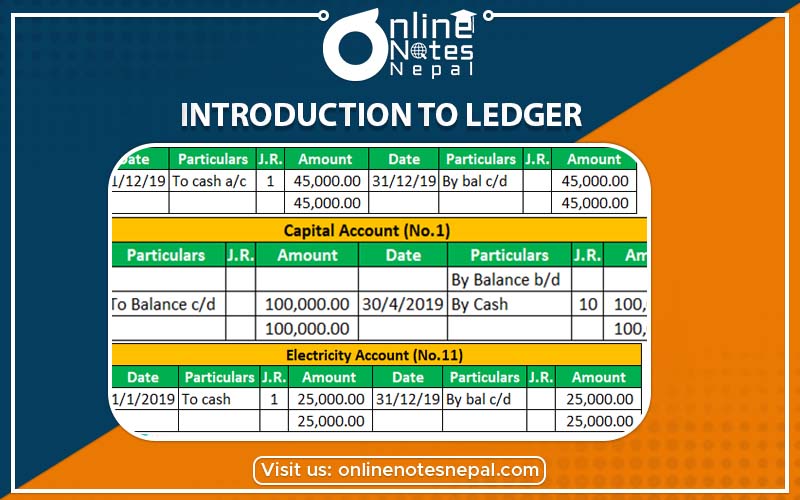
The journal cannot fulfill all the requirements of accounting. It registers all the transactions in the chronological order in the same place. It is the basis of preparing ledger accounts. It mixes up the records of different transactions due to which the position of a particular account cannot be reported. It fails to report the result of the transactions relating to a particular account during a period. So, ledger was introduced.
The ledger is the second step of accounting. It is the principal book of accounts. It contains all the accounts appeared in the journal or subsidiary books. It makes a classified record of all the transactions in summarized form. It is the final destination of all the accounts created in the primary books. It is the final source of all accounting information.The following are the main definitions of ledger:
"Ledger is a book of accounts which contains in a suitably classified form, the final and permanent record of trader's transactions." -V. J. Vickery
"A ledger is the most important book of accounts and is the final destination of the entries made in the subsidiary." -W. Pickles
From the given definition, we say that a ledger is a bound or register book which contain a large number of the account. It is the principal book of the account which make a final record of all the transaction in a classified manner.
A ledger account is simply a statement of information on a particular head. It is the summary records of all the transactions relating to a particular person or property or income or expenses. It is the details of the amount debited and credited to a particular person or income or expenses during a given period. The ledger account contains two sides which are debit and credit. Its left-hand side is called debit side and the right-hand side is called credit side. It shows the benefits on one side and sacrifices on another side for a given period. It is balanced and closed at the end of a given period to know the net effect or result.
The main objectives of ledger are as follows:
| Bases of differences | Journal | Ledger |
| Step | Journal is the first step of the accounting cycle. | Ledger is the second step of the accounting cycle. |
| Meaning | It is a primary book in which all the financial transactions are recorded in the same place. | It is a primary book in which all the transactions are posted in a classified manner. |
| Process | The process of recording transactions in a journal is called journalizing. | The process of transferring transactions from journal to the ledger is called ledger posting. |
| Basis | It is the basis for preparing ledger. | It is the basis for preparing trail balance. |
| Information | It provides detail information about the financial transactions. | It provides summary information about the financial transaction |
| Narration | It requires narration. | It does not require narration. |
| Result | It does not show the net result of the transactions performed. | It shows the net result of the transaction performed. |