Published by: Zaya
Published date: 06 Jul 2021
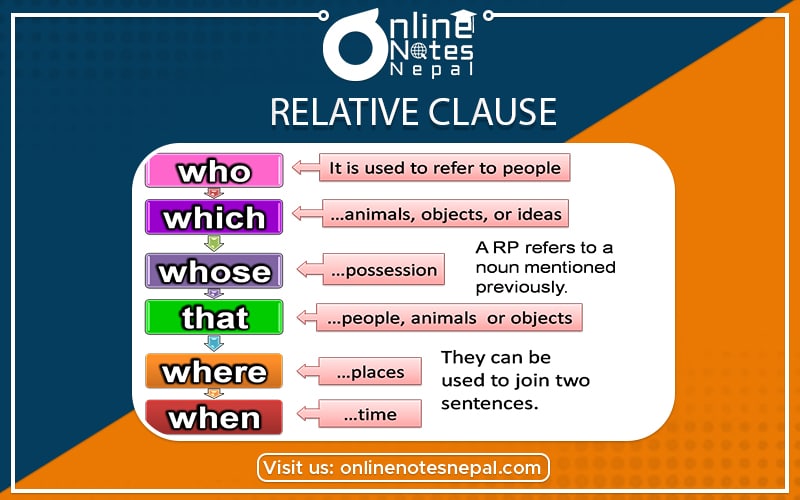
A relative clause is one kind of dependent clause. It has a subject and verb, but can't stand alone as a sentence. It is also called an “adjective clause”. Cause it functions as an adjective; it gives more information about a noun.
WH- words like where, when, who, which, etc are called a relative clause. We use relative clauses to give additional information about something without starting another sentence. By combining sentences with a relative clause, the text becomes more fluent and we can avoid repeating certain words. There are two types of relative clauses. They are:
E.g. He is the boy who helped the orphan children.
Aman, who works in a hotel, has decided to quit the job.
E.g. We met a friendly tourist who came from Australia. (no comma)
Yesterday I met Anjali, who told me about her father's business. (comma)
Mr. Koirala, who died in 1985, was a great singer.
E.g. I invited Ragini, whose brother is a good friend of mine.
E.g. We met everyone who passed the final exam.
E.g. I will meet you at 2 o'clock when you have a break at your school.
E.g, This is the year they should start working,
The place where they work is very nice.
E.g. This is the reason why these boys are weak.