Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 26 Jan 2022
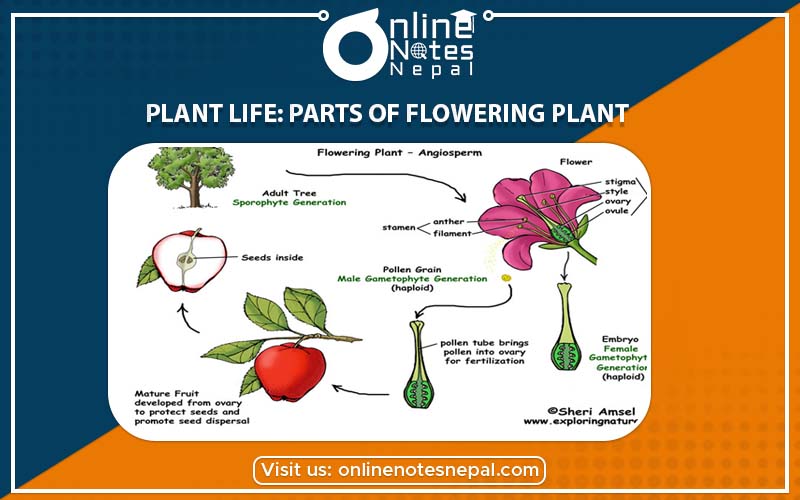
There are different types of plants around us. They differ in structure, habit, habitat etc. Some plants bear fruits and flowers whereas some plant does not bear flowers and fruits. Those plant which bears flowers er called flowering plant and those plant which does not bear flowers are called non- flowering plant. We call non- flowering plants as cryptogams and flowering plants as phanerogams. Phanerogams or flowering plants are the most advanced plant. Some of the examples of flowering plants are the sunflower, rose, marigold, lotus, etc. In this lesson, we discuss the parts of flowering plants. Flowering plants have two distinct parts. They are root system and shoot system.
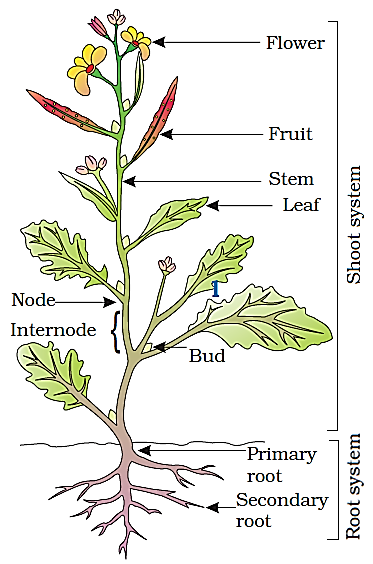
Root is a part of the plant the grows or remains underground. It fixes the plant to the soil. There are two types of roots. They are taproot and fibrous root. Dicotyledon plant has tap root whereas monocotyledon plant has fibrous root. In tap root, there one primary root that grows deep in the soil. It gives rise to other branches called secondary roots. The secondary root also gives out another root called tertiary root and branches of tertiary roots are called rootlets which are soft and delicate. It is covered by root cap. The rootlet also bears some hair- like structure called root hairs. Some of the examples of plants having tap root are carrot, mustard, turnip, radish etc.
Monocotyledon plants have fibrous root. Fibrous roots are not like tap root having primary root, secondary root, tertiary root etc but all the root hairs or the parts of root arise directly from the main same stem. They do not have root cap. They do not grow deep like tap root. These roots are found in mass or group. Some of the examples of plants having fibrous root system are grass, wheat, rice, banana, millet etc. Roots are the most important part of plants. It performs various important activities. Some of the function of roots are discussed below,
Shoot system is a part of plants that grows vertically above the ground or soil. The shoot system of plants includes stem, leaves, flowers and fruits. The shoot system is divided into two parts. The shoot system is responsible for photosynthesis, reproduction, transport, storage and hormone production. They are vegetative part and reproductive part.
Vegetative part include stem, branches and leaves.
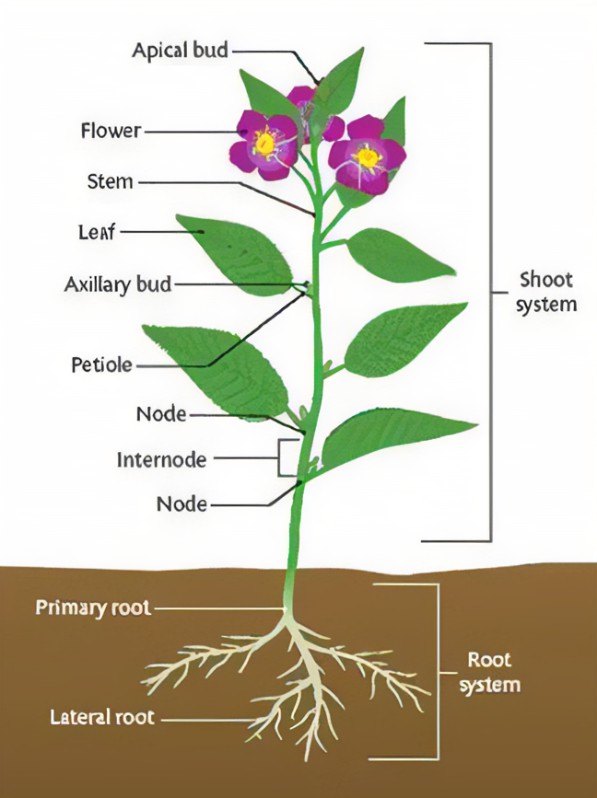
The stem: The stem is the main axis or aerial part of the plant that supports leaves and flowers. The stem develops from the plumule of the embryo of a seed. It gives rise to other branches known as lateral branches. The stems are thick at the bottom but gradually decreases its thickness from bottom to the top. There are some swollen points on the stem which are known as nodes from which the branches and leaves grow. The part of the stem between two nodes is called internode. Like this stem consists of branches, leaves, nodes and internodes.
There are also buds in the stem. There are two types of buds depending upon their positions. They are the axillary bud and terminal bud. The terminal bud is located at the tip of the stem and axillary bud is located at the axil of the plant (leaves). The axillary buds that grow into flowers are called floral buds. Apical bud helps in the increase of length or height of the plant.
The plant leaves are lateral outergrowth of the stem. It is thin and flattened. They grow from the nodes of the stem. They contain chlorophyll so they are green in colour. The leaves are one of the most important parts of the plant as it is the chief- food producing organ. A typical complete plant leaf consists of three parts. They are leaf base, petiole, and leaf blade. Leaf base is the base of the leaf through which the leaf grows. Near the leaf base, there is a narrow short stalk of the leaf that is attached to the stem which is known as petiole. Leaf blade or lamina is the flat and green portion of the leaf. Leaf blade is the broad flat part of the leaf. Most of the part of the leaf is made of the leaf blade. Photosynthesis takes place in leaf blade. The petiole attached to the leaf blade acts as a midrib that gives out branches known as veins. Veins provide mechanical support to the leaf and help in the transportation of water, mineral, and food into various parts of the leaf. The arrangement of veins in the leaf blade is called venation. There are two types of venation. They are reticulate venation and parallel venation. Dicotyledon plants have parallel venation and monocotyledon plant have reticulate venation. Leaf perform various activities. Some of the functions of leaf are discussed below,
Reproductive part of the plant is a flower.
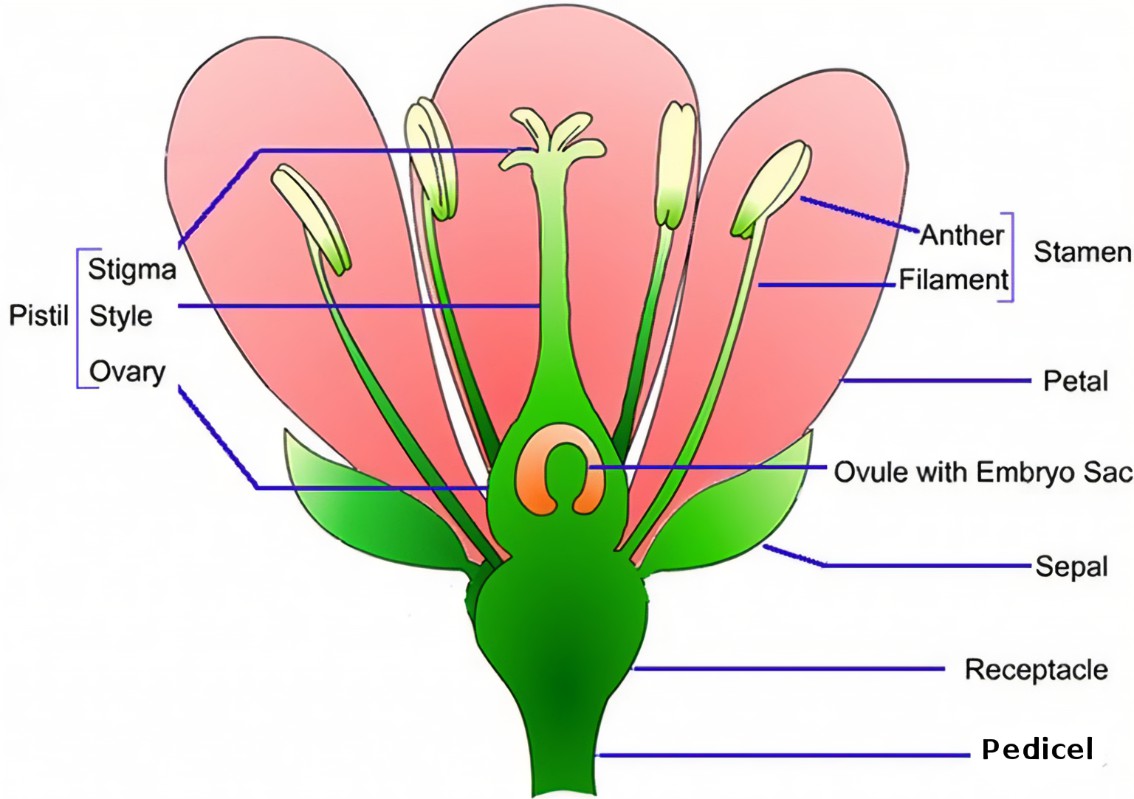
Flower is the reproductive part of most of the plants. In this lesson, we study about the different parts of flowers of the mustard plant. The flower of mustard plant is yellow in colour. It acts as a reproductive part. The flower of the mustard plants pedicilated, complete and bisexual. It has four parts which are calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium.
Calyx: It is the outermost part of the mustard flower. It is made of small, green leaf-like sepals. It protects the delicate inner parts of the flower bud and synthesizes foods. Sepals are free from each other. They are not joined or attached to each other.
Corolla: Corolla consists of a group of colourful petals. In a mustard plant, the corolla consists of four yellow petals. They are like sepals. The petals are also free from each other. The colour of corolla attracts insects and birds that pollinate the flower. The petals consist of two parts, claw, and limb.
Androecium: Androecium is the third whorl of a mustard flower that contains male reproductive structures called stamens. Stamen is composed of two parts, filament, and anther. The filament is a long, thin stalk of stamen whereas anther is the top of a stamen that produces pollen grains. In a mustard plant, there are six stamens which are arranged in two rings. The outer ring consists of two short stamens whereas the inner ring consists of four long stamens.
Gynoecium: Gynoecium is the fourth and innermost whorl of a flower that consists of the female reproductive part called carpels. Carpels are composed of three parts. They are the stigma, style, and ovary. Stigma is a top flat part of the carpel and ovary is a rounded structure located at the bottom of the carpel. The stigma and ovary are connected by the tube- like structure called style. The ovary contains ovules.
Depending upon the presence of androecium and gynoecium, there are two types of flower. They are the unisexual and bisexual flower. The flower is said to be a unisexual flower if it contains either male reproductive part (androecium) or female reproductive part (gynoecium). Some of the examples of plants having unisexual flower are coconut flower, papaya, watermelon, cucumber, maize, etc. The flower is said to be the bisexual flower if the flower contains both male reproductive part (androecium) and female reproductive part (gynoecium). Some of the examples of the bisexual flower are lily, rose, sunflower, tulip, tomato, mango etc.
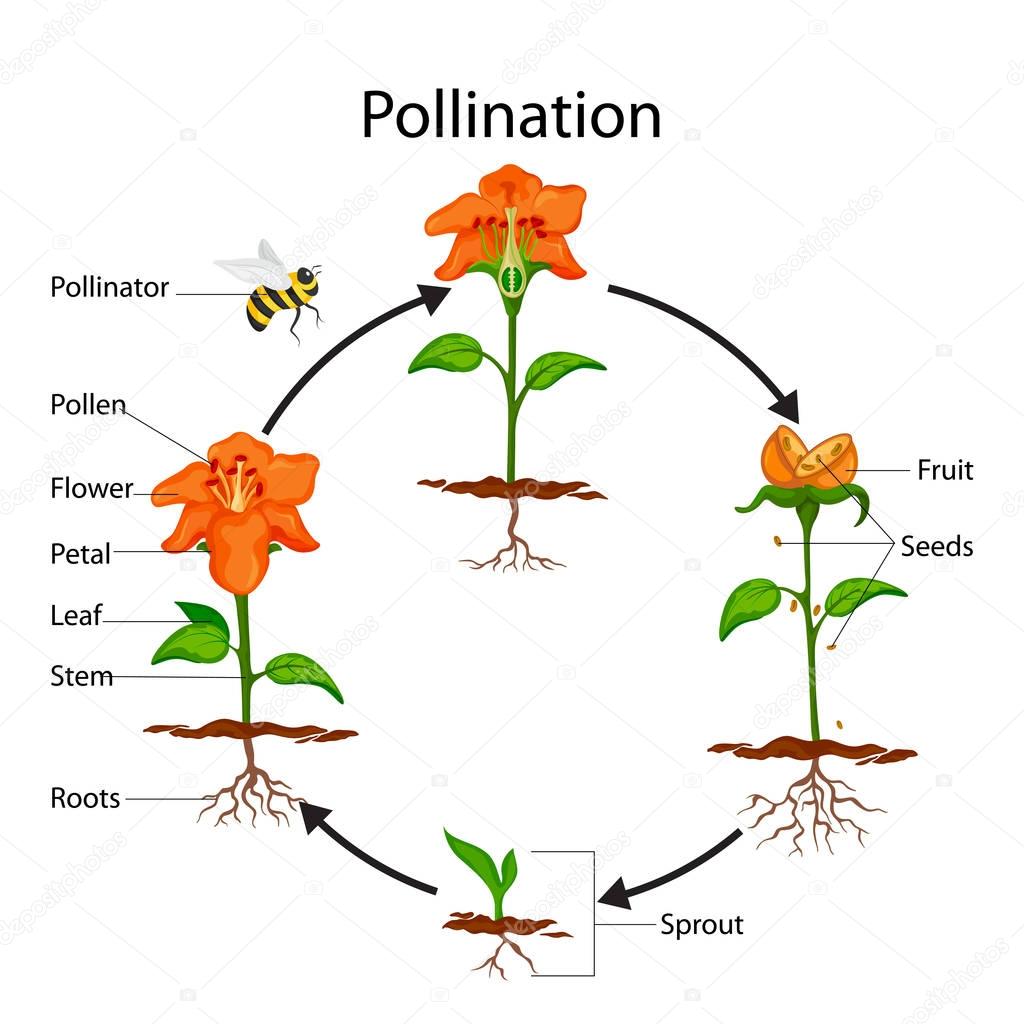
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or the different flower is called pollination. When the plants or the flowers becomes mature, the anther becomes dry and gives out pollen grains. These pollen grains are transferred by the pollinators like man, insect, birds, wind, etc from the anther to the stigma. Pollination is a prerequisite for fertilization. There are two types of pollination. They are self- pollination and cross pollination.
Self- pollination: The pollination is said to be self- pollination if there is a transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. It involves only one flower. This type of pollination occurs in bisexual flowers as it contains both male and female reproductive part. Some of the common examples of self- pollinating flowers are the rose, sweet peas, peppers tomatoes, orchids etc.
Cross- pollination: The pollination is said to be cross- pollination if there is a transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower of one plant to the stigma of a flower of another plant.It is more complex than self- pollination. For cross pollination, external agents or pollinators like insects, animals, wind etc are important. It occurs in both unisexual and bisexual flowers. Some of the examples of cross- pollinating flowers are apples, grapes, cherry, onions etc.
The union of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilization. When there occur pollination, the pollen grains or male gametes are deposited on stigma. When these pollen grains absorb secretions of stigma, it begins growing or germinating that produces pollen tube that grows down towards the ovary or the egg cell. The pollen tubes then penetrate the ovule, which contains female gametes.
The fertilization in flowering plants is called double fertilization because there is a fusion of two male gametes. One of the male gametes fuses with the egg cell forming zygote whereas the other one fuses with the secondary nucleus forming endosperm nucleus. When the fertilization completes, the zygote forms embryo and endosperm nucleus from the endosperm of the seed.
Here, an embryo is the first stage of development of plant and endosperm acts as a food storage tissue of the seed. The embryo and endosperm collectively make a seed.The ovule forms seed and the ovary forms the fruit after fertilization. A seed is capable of growing into a new plant if it gets favourable condition.