Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 26 Jan 2022
All the living organisms eat food for proper growth and development of their body. Food provides energy. When we eat food, only the useful materials are absorbed but the harmful materials are not absorbed. Various types of chemical reaction occur in our body to carry out life processes.The sum of these reactions is called metabolism. During metabolic activities, useful products along with harmful products are produced as a by- products. These harmful toxic products should be removed from our body.The removal of metabolic waste products from the body of an organism is known as excretion. Excretion can be defined as the process of removal of harmful products from our body that is formed as by- products during metabolic activities.
In unicellular organisms like an amoeba, the excretion takes place through their general body surface by the process of diffusion. There is no excretory organ in protozoa (aquatic habitat) but the excretion takes place through the plasma membrane by the process of diffusion. Talking about excretion in multicellular organisms like hydra, they remove their waste material from their mouth. The excretory organ of higher multicellular organisms and insects are tubular in a structure like in flatworms and leech. The kidney is the main excretory organ in vertebrates.

Plants do not have well- developed excretory system like in animals. Plants perform excretion by the different method. Plants take in carbon dioxide from stomata and lenticels present in leaves and stem. It throws out oxygen after taking in carbon dioxide which is the main excretory product of the plant. The gaseous waste materials produced during respiration and photosynthesis diffuse out through stomata in the leaves and through lenticels present in stem and roots. Similarly, various minerals and water used by plants are absorbed by the roots. The dissolved minerals remain in the plant cells whereas the excess water evaporates mostly from stomata and different aerial parts of the plant like stem, fruits, etc. This process of removal of water is known as transpiration. Therefore, transpiration can be defined as the process of the removal of excess water from leaves and other aerial parts of the plants in the form of water vapour are called transpiration.
In humans, the kidney acts as the main excretory organ but the skin, liver and lungs also help in excretion. The excretory system of the human body includes two kidneys, two ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra.
Organs that helps in Excretion: Organs like skin, liver and lungs also helps in excretion.
Lungs: It is a respiratory organ. It helps in the removal of carbon dioxide and water in the form of gases.
Skin: Our skin contains sweat glands. It helps in the excretion of small amounts of water, urea and salts.
Large intestine: It helps in the removal of solid waste products in the form of faecal matters.
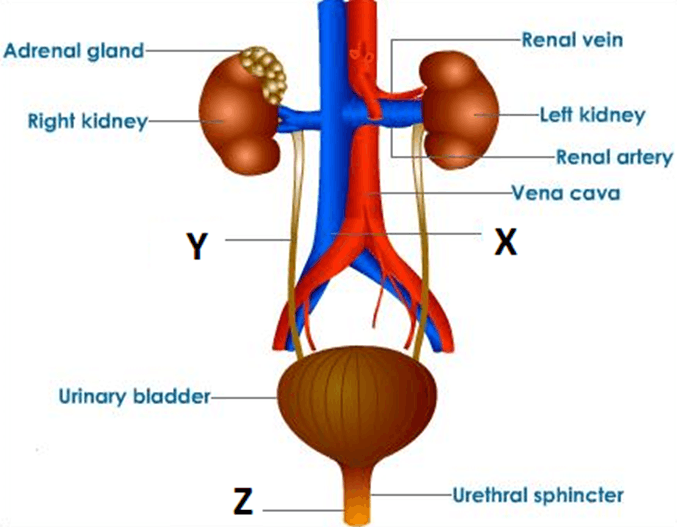
There are two bean- shaped kidneys that are located near abdominal cavity on each side of the certebral column. They are dark red in colour.Each kidney is about 10 cm long and weighs about 150 g.Each kidney is enclosed in a thin, fibrous covering called the capsule. Each kidney is made up of millions of coiled tubule known as nephrons. They are responsible for the separation of urine from the blood. The kidney collects waste materials from the blood and removes them as urine. The kidneys filter about 113 to 144 litres of blood to create 0.64 to 1.81 litre of urine every day, according to the National Institute of Health.
The ureter is a tubular structure that arises from each kidney. It opens into the urinary bladder. It is about 30 cm in length and 4 millimetres in wide. Its main function is to carry urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a muscular bag. The urine is transferred to urinary bladder from the kidney for temporary storage. When the urinary bladder gets filled, the bag contracts and the urine is passed out through the urethra. The urethra is a small tube that opens outside the body. In the summer season, there is no regular urination though we take lots of water because the water passes outside in the form of sweat. During the winter season, sweating does not occur so urination is regular. In the summer season, the urine is concentrated and more dark in colour whereas in the winter season, the urine is dilute and colourless.
All the living organisms such as human, animals, plants, bacteria etc must obtain nutrition from the environment in order to continue their life. They obtain nutrition from the foods that they eat. Different organisms have different method of taking food. The process of taking food is known as nutrition. There are two types of nutrition. They are autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition. In autotrophic nutrition, the organisms prepare foods by themselves where as in heterotrophic nutrition, the organisms depends on others for their food.They digest the food and get energy from the food which is utilized to perform various activities. But all the foods eaten by them are not digested or absorbed.This types of foods are called as waste materials. This waste materials should be removed from the body if not, they may be harmful for our body.
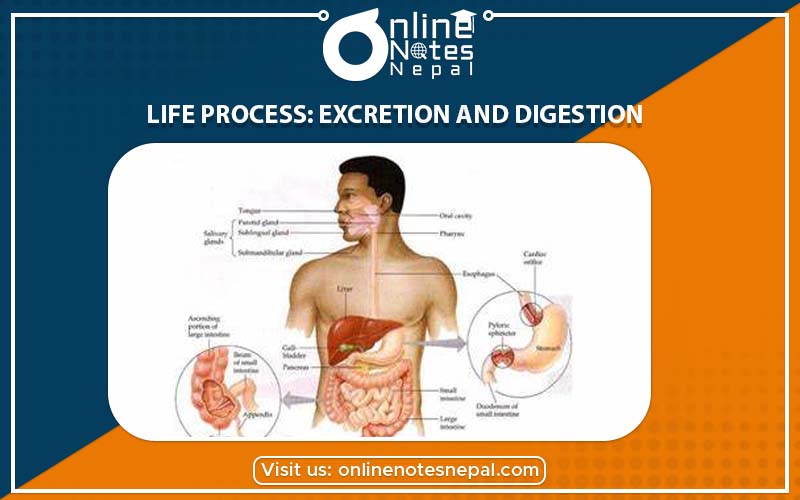
The human digestive system is a complex series of organs that converts food into essential nutrients that are absorbed into the body and remove unused waste material. The human digestive system includes two parts, alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal includes organs like mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.Digestive glands include the glands like salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gastric glands and intestinal glands that secrete digestive juices that are necessary for the proper digestion of food. Digestive system converts our meals into the body fuel. It helps in digestion and absorption of food. Digestion can be defined as the process of mechanical and chemical breakdown of ingested complex food into simpler ones.

Mouth is the first part of the alimentary canal or digestive system. In mouth, the foods are converted into small pieces by chewing with the help of teeth. This process is called mastication. The small pieces of foods are known as bolus. The tongue present in the mouth helps to swallow the food into the stomach. The mouth contains salivary glands that secrete salivary amylase called ptyalin which helps in the partial digestion of carbohydrates. The saliva also moistens the food.
The stomach is a muscular sac- like organ where food is temporarily stored. The stomach secretes various acids and enzymes that help in the further breakdown of food. It secretes the gastric juice that contains hydrochloric acid, pepsin and other enzymes. The mixture of foods with gastric juice is called chyme. HCL makes the medium acidic and helps in killing harmful germs. The pepsin helps in digestion of proteins whereas renin converts milk into casein. Now the foodpasses into the small intestine in the form of liquid or paste.
The small intestine is a long tube that is made up of three parts, duodenum, jejunum and ileum. In the small intestine, the liver secrete bile juice and pancreas secrete pancreatic juice. The bile juice makes the medium neutral or slightly alkaline. The pancreatic juice contains other enzymes like trypsin, amylase and lipase. Trypsin digests the protein, amylase digests the starch and lipase digest the fat.The nutrients are absorbed in the ileum of the small intestine.
It is the last part of the alimentary canal. It is also known as colon. It is wider then small intestine but shorter. The remaining things after digestion are passed into the large intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and vitamins while converting digested food into feces. After large intestine, the remaining things are passed to the rectum for egestion.
Digestion and absorption of food
| S.N. | Digestive organs | Digestive glands | Digestive juices | Enzymes | Function of digestive juices | Others |
| 1. | Mouth | Salivary glands | Saliva | Ptyalin | It converts starch into maltose. | It helps in chewing of food and digestion of starch. The food is passed from mouth to the stomach through food pipe in the form of bolus. |
| 2. | Stomach | Gastric juice |
HCl |
x Pepsin
|
HCl kills harmful germs and makes medium acidic Pepsin converts protein into peptone
|
It helps in storage of food and initial digestion of proteins and fats. Various gastric juice (pepsin, HCl, renin) acts on food. Here. the food changes into chyme. |
| 3. | Duodenum |
Liver Pancrease |
Bile juice Pancreatic juice |
x
Trypsin
|
Bile juice emulsifies fat and makes medium neutral or slightly alkaline
Trypsin converts peptones into peptides Amylase converts starch into maltose |
|
| 4. | Small intestine | Intestinal gland | Intestinal juice |
Erepsin Sucrase Lactase Maltase |
Erepsin converts peptide into amino acids Sucrase converts sucrose ino glucose Lactase converts lactose into glucose Maltase converts maltose into glucose |
It helps in complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. Nutrients are absorbed completely through villi. |
| 5. | Large intestine | x | x | x | It absorbs water and vitamins. | It helps in absorption of water, production of vitamins and storage of undigested food. |
Different organs of alimentary canal like mouth, stomach, large intestine etc are involved in digestion of food. But one of the most important part of digestion of food i.e. the absorption of food takes place in small intestine or in ileum which is part of small intestine. The wall of small intestine contains small finger- like projection which is known as villi. They increase surface area for the absorption of food. They are richly supplied by the blood capillaries. They helps in absroption of digested food by the process of diffusion. The absorbed foods are then sent to the different parts of body through the blood.
When the food is completely digested, important food materials are absorbed. These absorbed food materials are carried by bloods which are used by different parts of the body in a various ways. The food molecules carried by the bloods are absorbed by our body cells. This is known as assimilation. Assimilation can be defined as the use of absorbed nutrients in the formation of new protoplasm.
Not all the foods are digested or absorbed. Some undigested food materials and remaining things after digestion and absorption are left over in the body. These remaining food materials are removed from the body through rectum and anus. This process is known as egestion. Therefore, egestion can be defined as the process of eliminating the remaining things after digestion and absorption of nutrients.