Published by: Nuru
Published date: 02 Dec 2021

In this topic Magnetism and Electricity, we discuss about the magnets, molecular theory of magnetism, magnetic induction, cells combinations, house wiring.
Magnetism is physical phenomenon that is mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field.
Properties of magnets are:
Molecular theory of magnetism:
It states that, "If molecular magnets align in a row, then the substance exhibits properly. If they are kept haphazardly, they do not exhibit magnetic property."
The poles of magnets annot be seperated even by breaking into pieces because they exist in a pair and every molecule of a magnet has poles in the pair.
Evidence of molecular theory of magnetism:
Magnetic Induction:
Magnetic Induction is the process by which substances like iron are magnetized by the magnetic field. the magnet causes the individual particles of the iron, which act like tiny magnets, to line up so that the sample as a whole becomes magnetized.
Demagnetization:
Demagnetization means decreasing magnetic property or losing it completely. In these conditions, magent loses its property.
Ways to prevent from demagnetization:
Cell is a device where a potential difference between two conductors is maintained by conversion of chemical energy into elctrical energy. A cell consists of two metal rods called electrodes dipped in a solution called electrolyte.
when the cell is in pen circuits, the potential difference between electrodes is called its electromotive force(e.m.f). the stength of the e.m.f., ehich a cell can produce in agiven circuit, depends on the e.m.f.
The e.m.f of cell depends on:
| Dry Cell | Simple Cell |
| Invented by Laclanche Georges in 1865. | Invented by Alessandro Volta in 1800. |
| It contains a zinc container, as a negative terminal, and electrolyte is a paste of ammonium chloride. Carbon rod with a brass cap serves as the positive electrode surrounded by a mixture of powdered manganese dioxide and carbon particles. | It contains two plates, one copper, and one zinc, both dipped in dilute sulphuric acid and taken in the glass container. Zinc and copper are electrodes and dilute sulphuric acid is the electrolyte. |
| It can be charged and used again for lighting puposes in vehicles, emergency lights. | Not suitable for torch cells as potential difference is 1.08 V. |
| It is cheaper and compact than simple cell. | It is expensive in comparison to dry cell. |
Arrangement of the cells which is designed to get the maximum potential difference and current supply is called combination of cells. In general they can be grouped as:
Series combination of cells:
In this combination the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the other cell.
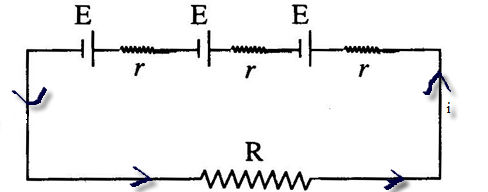
Total potential in this case (V) = sum of the individual p.d of the cell.
The current in the external resistance is the number of times the current due to t e single cell
Parallel combination of cells:
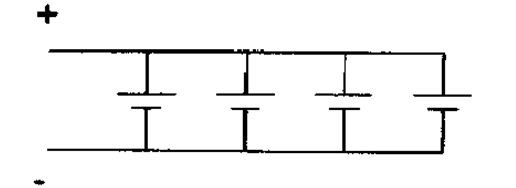
The cells are said to be parallel if the positive terminal of all cells are connected at one common point and the negative terminal are connected to one common point.
In parallel combination of cells the total voltage between any two points is always constant this is equal to the voltage of one cell.
The difference between parallel and series combination of cell is given below:
|
Parallel Combination |
Series Combination |
|
In parallel combination, the negative terminals of all the cells are connected at one side and the positive terminals of all the cells are connected on the other side. |
In series combination, negative terminal of one cell is connected to positive terminal of another cell. |
In Nepal, there are two wires; one live wire or phase wire, and neutral wire. The live wire acts as a positive terminal and neutral wire acts as a negative terminal. Both are connected to a meter box in our house, also the live wire has fused associated with it. Normal capacity is 15 A of this fuse, but can be increased or decreased as regarding with the needs.
Those line are taken into a switch fuse for each line is taken out, that regulates current going into each room or distribution board. Also, earthing is added in our house wiring.
MCB is imprved and extended version of the fuse which automatically switches off the eclectrical circuit during the abnormal condition of the network means overload condition and faulty condition. The fuse does not sense, but MCB does it in more reliable way. In fuse system, fuse needs to be changed after short circuit, but now we don't need to change the MCB also after short circuit.