Published by: Nuru
Published date: 18 Nov 2021
In this topic, cells and tissue we discussed about the brief description of Cells and Tissue for Grade 8 Science Notes. It is a Reference notes for Grade 8.
The bodies of all living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. They are capable of performing all the essential functions of life for the survival of living organisms.
A cell is defined as a structural and functional unit of life. In unicellular organisms, all the important functions of life like respiration, digestion, excretion, reproduction, etc are performed within single cell. But, in multicellular organisms, there are seperate groups of cells responsible for the seperate functions. Such groups of cells response for seperate functions. Thus, tissue is the group of cells which have similar structure and perform the similar function. In higher organizations, group of tissue organize to form organs. A large number of organs co-ordinate to form a system.
Four different types of tissues are found in animal. they are:
1. Epithelial Tissue:
They are covering tissues. They cover the body surface, organs, ducts, blood vessels, and body cavities.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
Functions of Epithelial Tissue:
Types of Epithelial Tissue:
Epithelial Tissues can be divided into two types:
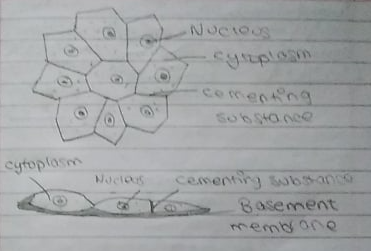
Simple Epithelium:
SImple Epithelium consists of single layer of cells, all of which are in contact with basement membrane. Compound epithelium consists of more than one layer.
Types of Simple Epithelium
1. Pavement Epithelium or Squamous Epithelium:
It is formed of thin, flat, polygon cells which fit like the tiles in a floor. It is found in skin, blood vessels, alveoli of lungs, body cavities, etc.
2. Columnar epithelium
It is formed of tall pillar like cells lying side by side. The cells are attached to the basement membrane. It forms the lining of digestive system from stomach to anus.
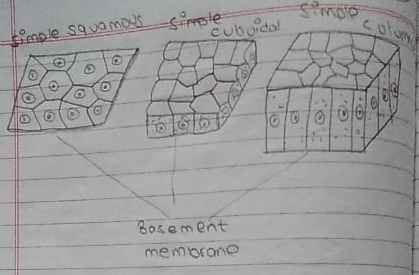
3. Cubical epithelium
It consists of cube shaped cells fitting closely together lying on basement membrane. It is found in thyroid gland, tubules of kidney, inner part of ovary, duct of sweet gland, etc.
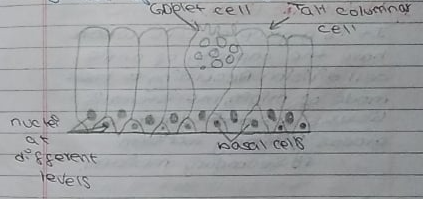
4. Glandular epithelium
It is the modification of columnar epithelium in which cells have become specialized for the production of chemical substances which are essential for different activities of life. They are present in various glands of the body.
Plant tissue can be divided into two types:
Meristematic Tissue:
It is a group of cells which have the capacity of active cell division. According to their mode of origin, meristematic tissues are divided into two groups:
Primary meristem
The meristematic tissues that originate from the embryonic stage of plants are called primary meristems. These meristem continue to divide throughout the life of plant. On the basis of position, the primary meristems are divided into three types:
Apical meristem:
They are present at the tip of root, stem and branches. They help to increase the length or height of plant or its branches. When the tip of plant is cut, its height stops to grow because apical meristem is lost.
Intercalary meristem:
They are found at the base of leaves above the nodes. It increases the length of internodes.
Lateral meristem:
They are present along the side of stem and root. They are responsible to increase the thickness of stem and root.