Published by: Nuru
Published date: 02 Dec 2021

In this topic Light, we discussed about the definition of light, ray and beam, types of mirror, lens and its types, ray diagram of convex lens and concave lens.
Light is the form of energy that can be found in nature from the sources like sun and other artificial sources.
Ray: A ray is a hypothetical stream of light. A ray is a concept, which cannot be observed physically, and the ray has a zero width. Rays are only discussed under light.
Beam: A beam is a thin projection of particles or waves. A beam is a finite width, and it can be observed physically. Beams are discussed both in wave and particles.
Incident ray: The ray which comes to strike on the surface is called incident ray.
Reflected ray: the light coming back after striking the surface of the plane mirror is called reflected ray.
Mirror is an object that reflects light in such a way that you can see your image in it. It may be real or virtual, erect or inverted, and diminished or enlarged.
Types of Mirror:
Plane mirror is a mirror with a flat refractive surface. We use the plane mirror as a looking glass. Plane mirrors are the only type of mirrors for which a real object always produces and image that is virtual, erect and of the same size as the object.
Spherical mirror is a mirror which is polished, reflecting surface a part of hollow sphere of glass. One side of it is made opaque and another side acts as a reflecting surface.
Depending on the nature of reflecting surface of the mirror, there are two types:
| Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
| A spherical mirror whose inner hollow surface is the reflecting surface is called concave mirror. | A spherical mirror whose outer bulging surface is the reflecting surface is called convex mirror. |
| It may give magnified or diminshed image. | It forms diminished image(smaller in size only). |
| The image formed is real except when the object is between focus and principal. | The image is always virtual. |
| It is used in shaving glass, car headlights, projectors. | It is used for diverging the light over a large area and placed as a street light. |
Terms used in spherical mirror:
Pole: It is a geometrical centre of the surface of a mirror. It is represented by a point P.
Center of curvature: It is the radius of the hollow sphere of which mirror is a part represented by C.
Radius of Curvature: It is the radius of the hollow sphere of which mirror is a part, denoted by R.
Principal axis: The line joining the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature and produced on both sides is called the principal axis.
Principal focus: The point on the principal axis where a beam of light incident to spherical mirror parallel to the principal axis converges or appears to be diverging from after reflection, is called the principal focus. It is denoted by F. The picnipal focus is real in the concave mirror and virtual in case of a convex mirror.
Focal length: It is the distance between the principle focus and pole of the mirror. It is denoted by f. The focal length is half the half of the radius of curvature.
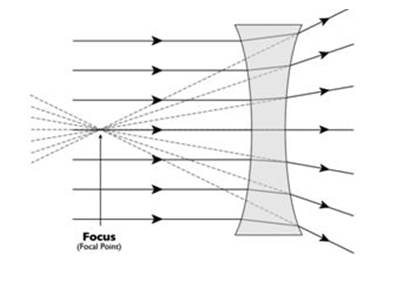
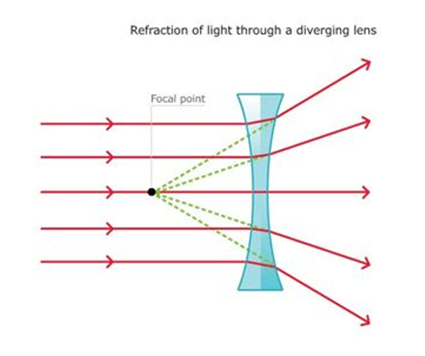
This lens is thin at its centre than at edges. Diverging lens is also called concave lens. It is thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges and has virtual focus.
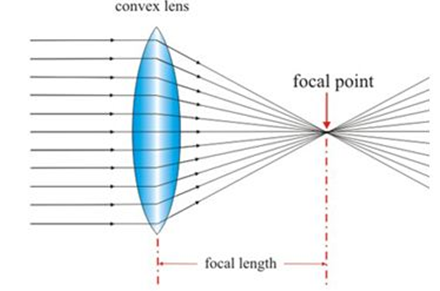
This lens is thick at its centre and thin at its edges .A convex lens is called converging lens because it converge rays of light passing through it at a point after refraction.
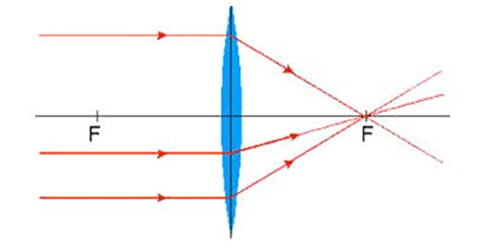
Real image and virtual image:
a. Parallel rays coming from the infinity meet at the focus after refraction by convex lens. The nature of image is real inverted and diminished.
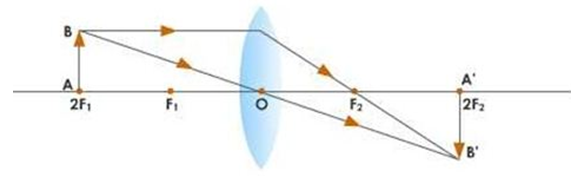
b. When the object is placed beyond the 2F, real inverted and diminished image is formed between F and 2F
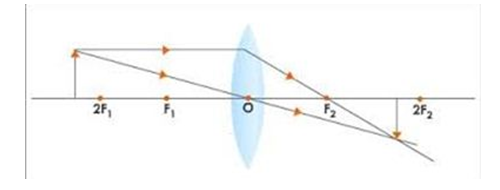
c. When the object is placed at 2F, the nature of the image is real, inverted and of the same size
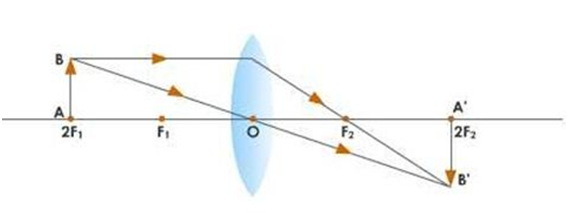
d. When the object is placed between 2F and F the image is formed beyond the 2F which is real, inverted and magnified.
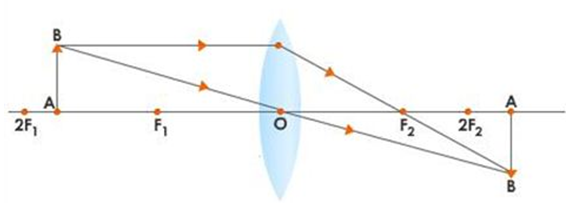
e. When the object is placed at focus the image is formed at infinity which is real inverted and magnified.
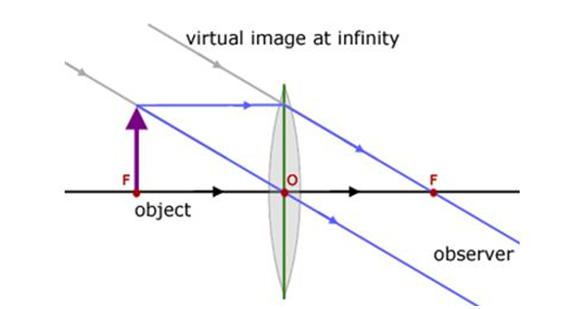
f. When the object is kept at optical centre and focus, virtual magnified and erect is formed.
When the object is kept between infinity and focus, virtual erect and diminished image is formed between the focus and optical centre on the same side of the object in the lens.
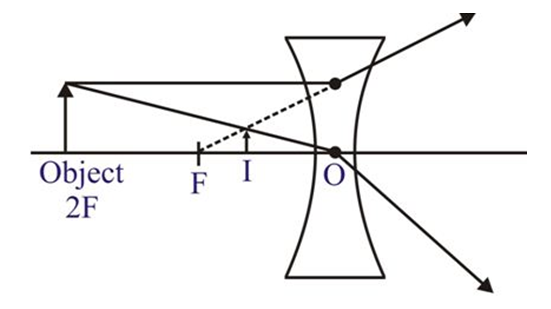
When the object is kept infinity, virtual erect and highly diminished image is formed at focus.
Magnification:
The ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object is called magnification.
Refraction of Light:
Light travels in a straight path as long as it is travelling in a single medium only. When a ray of light travles from one medium, it bents. The bending of light when it is passed from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light. The medium which possesses high density is called denser medium, and the medium which possesses less density is called rarer medium. For example; in water and air, water is denser medium and air is the rarer medium. In glass and water, glass is denser, and water is rarer medium. Thus denser and rarer medium are relative terms.