Published by: Nuru
Published date: 03 Dec 2021
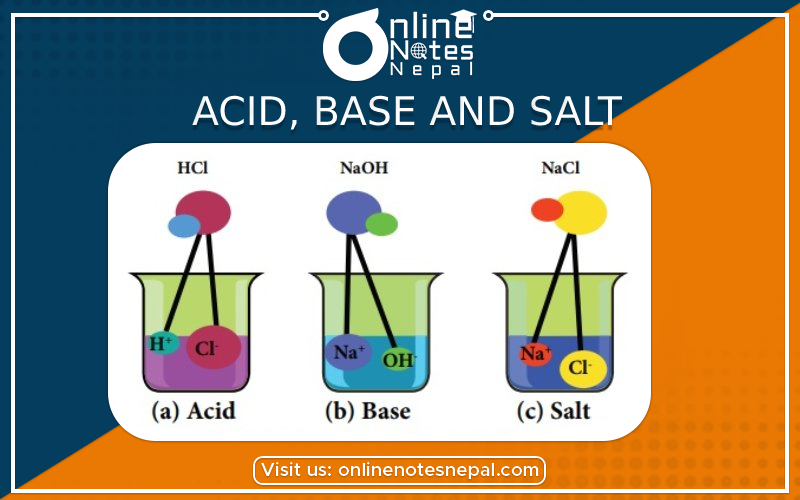
In this chapter, we discuss about the introduction, properties, uses in daily life of Acid , Base, and Salt in Grade 8 Science. Reference Notes for Grade 8.
Acid is a substance which gives hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. For examples, Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3), carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Acid is also defined as a substance which dissociates in water to give positively charged hydrogen (H+).
Disaccociation of HCl is given as: HCl :- H(+) + Cl(-)
Disaccociation of acetic acid in aqueous solution is: CH3COOH :- H(plus) + CH3COO(minus)
Inorganic compounds can be classified into three main classes namely acids, bases, and salt on the basis of their own properties.
Properties of acids:
a) Acid is sour in taste.
b) Acid reacts with base to give salt and water.
For example:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
(acid) (base) (salt) (water)
c) It gives hydrogen ion (H+) when dissolved in water.
For example:
HCl → H+ + Cl-
d) Acid turns blue litmus paper to red, light yellow color of methyl orange to red and phenolphthalein to colorless.
e) When acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates, carbon dioxide is produced.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
f) They react with metallic oxides to give salt and water.
Na2O + 2HNO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O
Sodium Oxide + Nitric Acid → Sodium nitrate + Water
g) Dilute acids decompose bicarbonate and carbonates and liberate carbon dioxide.
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
Characteristics of acid:
They all contain hydrogen
Many acids are corrosive.
They turn blue to red litmous paper.
They turn methylorange into yellow color.
Uses of acid:
Bases are the substance, which gives hydroxyl ions (OH-) when dissolved in aqueous solution.
For example: Sodium oxide (NaO), Potassium hydroxide (KOH) etc.
Sodium hydroxide and ammonia are bases because they give hydroxyl ions in water.
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
Sodium hydroxide
NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-
Ammonia (Ammonium ion)
Bases which are soluble in water are called alkalies. Some bases are not soluble in water. They are not alkalies. Thus, all alkalies are bases but all bases are not alkalies. Sodium oxide is called soda and potassium hydroxide is called caustic potash.
| Bases | Formula |
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH |
| Potassium hydroxide | KOH |
| Aluminum hydroxide | Al(OH)3 |
| Ammonium hydroxide | NH4OH |
| Sodium oxide | Na2O |
| Potassium oxide | K2O |
| Magnesium oxide | MgO |
Properties of base:
Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
Some bases used in daily life:
| Bases | Uses |
| Sodium hydroxide | In the manufacture of soap. |
| Potassium hydroxide | Firewood ash-filtered wood ash is used for washing clothes in rural areas. |
| Aluminum hydroxide | As medicine (antacid) for gastric patients. |
Differene between acids and bases:
| S.N | Acids | Bases |
| 1. | Turn blue litmus into the red. | Turn red litmus into blue. |
| 2. | React with metals to give a salt and hydrogen gas. | Normally do not react with metals. Only some metals like zinc, aluminum and tin react to give hydrogen. |
| 3. | Are corrosive to skin. | Are slippery to touch. |
| 4. | Are sour in taste. | Are bitter in taste. |
| 5. | React with bases to give salts and water. | React with acids to give salt and water. |
| 6. | Aqueous solutions of acids contain replaceable hydrogen ions. | Aqueous solution of the base contains replicable hydroxyl ions. |
| 7. | Give no color with phenolphthalein. | Give red color with phenolphthalein. |
Salts:
Salts are the neutral compounds, which are formed by the reaction between acid and base. Example: NaCl, CaCL2 etc.
The salt formed by the complete displacement of hydrogen atoms by a metal or electropositive radical is called normal salt. Normal salt are neutral in nature. For e.g.: NaCl, KNO3 etc
The salt formed by strong acids and weak base are strong salt. Example; CuSO4
The salt formed by weak acid and strong base are called basic salt. Example; Ca(HCO3)2
Properties of salts
Preparation of salts
Salts can be prepared in many ways. Some methods of preparing salts are given below:
Some salts and their uses are given below:
| Salts | Uses |
| Sodium chloride | As edible salts (table salt, rock salt) |
| Copper sulphate | As insecticides |
| Magnesium sulphate | Used in constipation |
| Calcium sulphate | Plastering fractured bones, in the manufacture of chalk. |