Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 02 Jul 2021
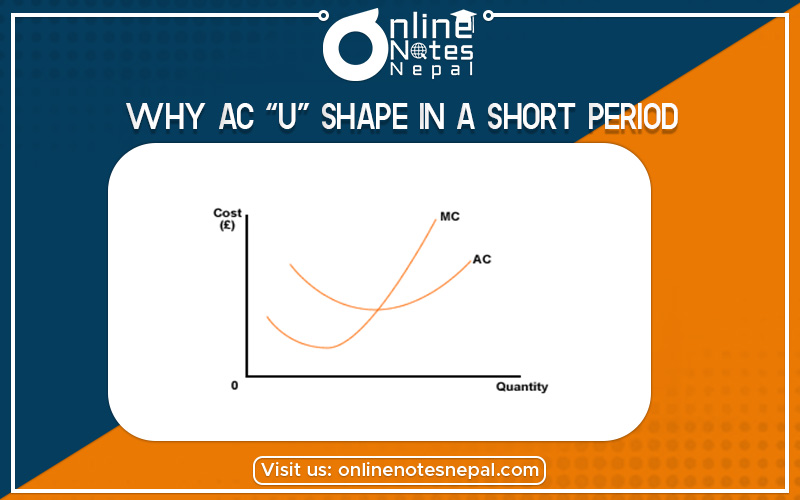
Why AC “U” shape in a short period it can be explaining below.
The average cost can be obtained from dividing total cost by the quantity of output. It is also called total coast (TC) per unit of output. The short-run average cost curve of a firm is “U” shaped. It means as output rises, the factor of production are less utilized in the beginning. Therefore they cannot a product at an optimum level, so the average cost (AC) of output is high at the beginning. But when the production increases there rises different kinds of internal as well as external economize such as fall utilization of plant, division of labour, improvement of managerial skill, technical and marketing economize, etc. due to the above reason average cost decline up to the certain level of output. After the level of output there rises internal and external, this economizes such as overutilization of plant, overstaffing, mismanagement, etc, due to this reason average cost start rise. So the short-run average cost curve is “U” shaped. It can be explained by the following figure.
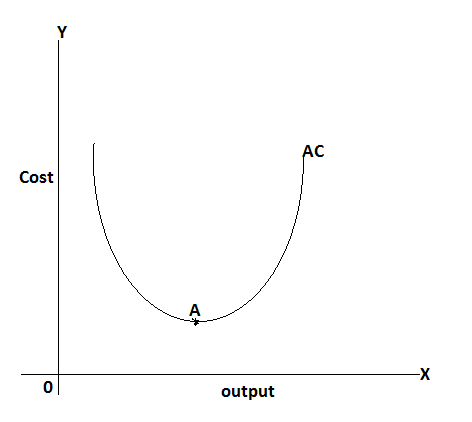
In this figure when a firm increases its output it gets economize and the result is a decline in AC. After the point of optimum condition, in figure point, An economize turn diseconomies and the result is increased in AC. This is the stage of the law of diminishing returns, so the short-run average cost curve is “U” shaped.
The relation between AC and MC
The average cost can obtain from dividing total cost by the quantity of output and marginal cost can be obtained from addition made to total cost by the production of an additional unit of the commodity. The relation between AC and MC can be explaining by the following figure.
The main points of the relation between AC and MC are as follows.