Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 02 Jul 2021
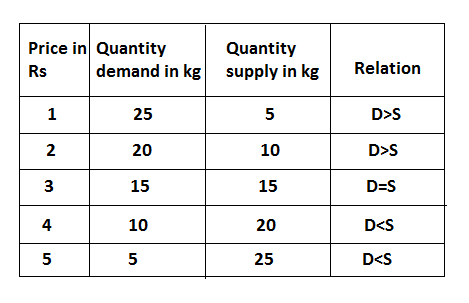
The process Price and output determination under perfect competition market can be explained with the help of demand, supply approach. The demand, supply approach price of the commodity is determined by the forces of market supply and market demand. In other words, the price is determined by the industry. Equilibrium of the commodity is determined at that point where the market demand of the product is equal to its market supply. The process of price and output determination can be explained with the help of the following table.
Price and Output Determination Under Perfect Competition Market || Perfect Market || Onlinenotesnepal
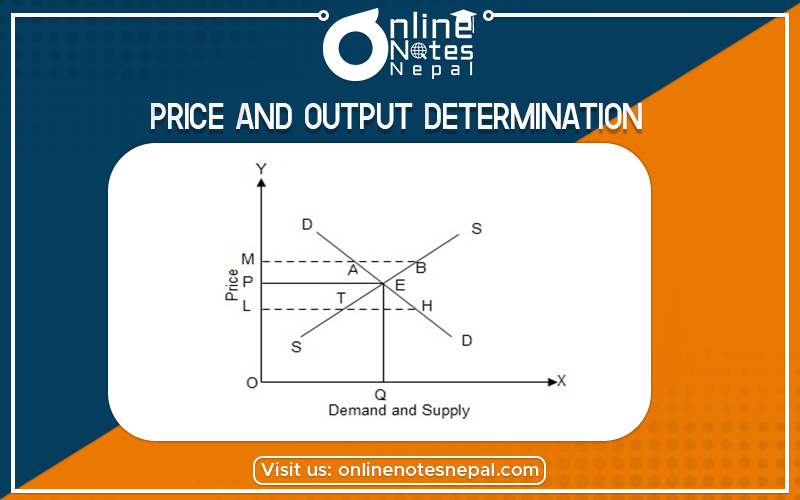
The above table shows the inverse relationship between market price and market demand and the positive relation between market price and market supply. When the price is Rs 3 the quantity demand and quantity supply are equal (15, 15) sp Rs 3 it the equilibrium price and 15 kg output is the equilibrium quantity. The price of the commodity will be determined when the supply and demand are equal to each other. It can be explaining by the following figure.
Price and Output Determination Under Perfect Competition Market || Perfect Market || Onlinenotesnepal
In this figure, DD and SS are the demand and supply curve. Point E is the equilibrium point where the equilibrium price level op and equilibrium output OQ determined. There is excess supply by AM amount if price rises from OP to OP2 thus there will be pressure to fall in the price unless and until quantity demand becomes equal to quantity supply at OP price. When the industry decreases the price from OP to OP1 there is excess demand over supply by BN amount as a result industry will raise the price until quantity demand becomes equal to quantity supply at OP price. Finally, the industry will be in equilibrium at point E where equilibrium price OP and output is OQ.