Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 02 Jul 2021
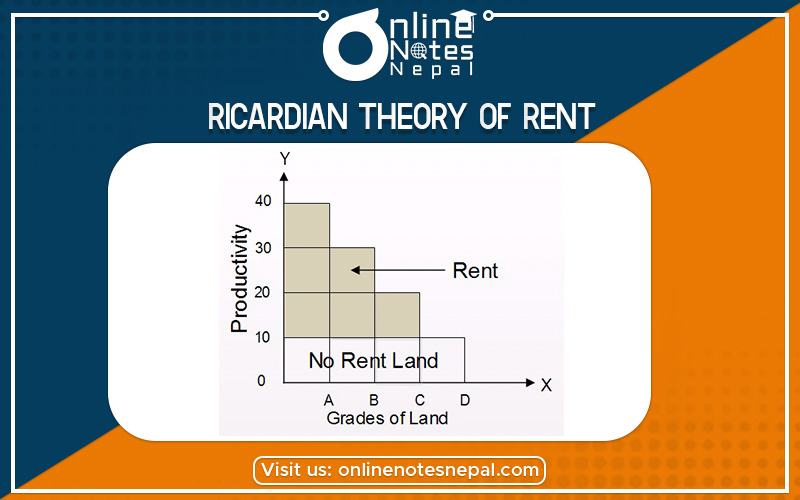
Ricardian theory of rent was propounded by classical economist David Ricardo this theory based on agriculture production on land. This theory of rent is also known as the classical theory of rent. According to David Ricardo rent is that portion of the produce of the earth which is paid to the landlord for the use of original and indestructible power of the soil. Thus Ricardo emphasizes that rent is a reward for the service of land which is fixed in supply. Rent rises due to the original quality of land, which is the indestructible Ricardian theory of rent based on the following assumption.
In the above assumptions, Ricardo explains this theory of rent Ricardo assumed that land and its fertility differ from place to place. The land of higher fertility gets higher rent that less fertile land. The least fertile land is known as marginal land or no rent land. Ricardian theory of land explains by the following table and diagram.
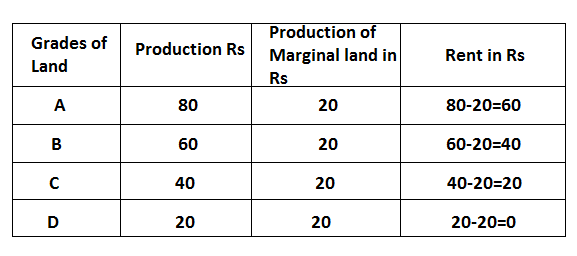
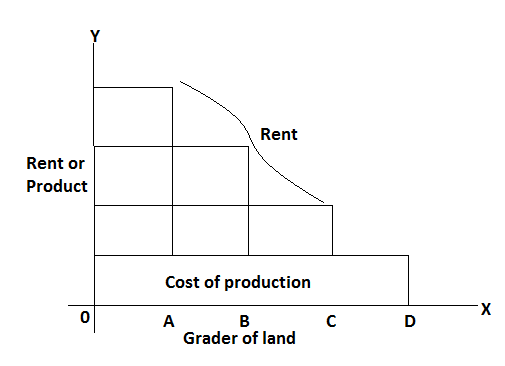
The above table and diagram show the calculation of rent. Here,
Land A 80-20=60
Land B 60-20=40
Land C 40-20=20
Land D 20-20=0
The above explanation is for extensive cultivation land however Ricardian theory is also equally applicable in case of intensive cultivation due to the operation of the law of diminishing return.